HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value)
HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value) – defines a type of color space. It is similar to the modern RGB and CMYK models. The HSV color space has three components: hue, saturation and value. ‘Value’ is sometimes substituted with ‘brightness’ and then it is known as HSB. The HSV model was created by Alvy Ray Smith in 1978. HSV is also known as the hex-cone color model.
Hue
In HSV, hue represents color. In this model, hue is an angle from 0 degrees to 360 degrees.
| Angle | Color |
|---|---|
| 0-60 | Red |
| 60-120 | Yellow |
| 120-180 | Green |
| 180-240 | Cyan |
| 240-300 | Blue |
| 300-360 | Magenta |
Saturation
Saturation indicates the range of grey in the color space. It ranges from 0 to 100%. Sometimes the value is calculated from 0 to 1. When the value is ‘0,’ the color is grey and when the value is ‘1,’ the color is a primary color. A faded color is due to a lower saturation level, which means the color contains more grey.
Value
Value is the brightness of the color and varies with color saturation. It ranges from 0 to 100%. When the value is ‘0’ the color space will be totally black. With the increase in the value, the color space brightness up and shows various colors.
Applications of HSV
The HSV color space is widely used to generate high quality computer graphics. In simple terms, it is used to select various different colors needed for a particular picture. An HSV color wheel is used to select the desired color. A user can select the particular color needed for the picture from the color wheel. It gives the color according to human perception.
HSV Representations
The HSV color wheel is used to pick the desired color. Hue is represented by the circle in the wheel. A separate triangle is used to represent saturation and value. The horizontal axis of the triangle indicates value and the vertical axis represents saturation. When you need a particular color for your picture, first you need to pick a color from the hue (the circular region), and then from the vertical angle of the triangle you can select the desired saturation. For brightness, you can select the desired value from the horizontal angle of the triangle.
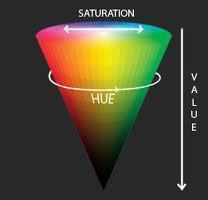
Sometimes the HSV model is illustrated as a cylindrical or conical object. When it is represented as a conical object, hue is represented by the circular part of the cone. The cone is usually represented in the three-dimensional form. The saturation is calculated using the radius of the cone and value is the height of the cone. A hexagonal cone can also be used to represent the HSV model. The advantage of the conical model is that it is able to represent the HSV color space in a single object. Due to the two-dimensional nature of computer interfaces, the conical model of HSV is best suited for selecting colors for computer graphics.
The application of the cylindrical model of HSV color space is similar to the conical model. Calculations are done in a similar way. Theoretically, the cylindrical model is the most accurate form of HSV color space calculation. In practical use, it is not possible to distinguish between saturation and hue when the value is lowered. The cylindrical model has lost its relevance due to this and the cone shape is preferred over it.
Advantages of HSV
The HSV color space is quite similar to the way in which humans perceive color. The other models, except for HSL, define color in relation to the primary colors. The colors used in HSV can be clearly defined by human perception, which is not always the case with RGB or CMYK.
HSV Alernatives
RGB, CMYK and HSL are some f the alternative models of color space.


Comments - One Response to “HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value)”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.