In comparison to the logical structure, which performs administrative tasks, the Active Directory physical structure checks when and where logon and replication traffic occurs. The physical structure of Active Directory contains all the physical subnets present in your network like domain controllers and replication between domain controllers. The physical structure of Active Directory: Domain Controllers: These computers run Microsoft Windows Server 2003/2000, and Active Directory. Every Domain Controller performs specific functions like replication, storage and authentication. It can support maximum one domain. It is always advised to have more than Read More
Global Catalog in Active Directory
Domains and Forests can also share resources available in active directory. These resources are searched by Global Catalog across domains and forests and this search is transparent to user. For example, if you make a search for all of the printers in a forest, this search goes to global catalog server for its query and then global catalog returns the results. Without a global catalog server this query needs to go to every domain in the forest of its result. It is important to have a global catalog on at Read More
Publishing Resources in Active Directory
What Resources can be published in Active Directory When you make Active Directory objects available to users, you are publishing the Active Directory resource. The resources that can be published in Active Directory include the Active Directory resources listed below: User objects Computer objects Printer objects Folders and files Network services The two primary published objects are printers and shared folders. Publishing information on shared network resources such as printers, folders, and files; eases the process of users locating these resources. Having resource information in Active Directory makes it easy Read More
Planning a Group Policy Strategy
On Overview on Group Policy Before you can consider to even begin planning a Group Policy implementation in your organization, you have to understand a few important aspects of Group Policy. Microsoft initially introduced group policies in Windows NT to assist administrators in managing the desktop configuration settings of users and computers. Windows Server 2000 included hundreds of Group Policy settings which you could configure. Windows Server 2003 offers all the group policies included with Windows 2000 as well as more group policies, which enable you to use new Windows Read More
Active Directory Security Principal Accounts
Understanding Active Directory Security Principal Accounts Active Directory consists of a considerable number of objects, and variety of objects, of which, security principal accounts are one. Security principal accounts are Active Directory objects that are assigned unique security identifiers (SIDs), and are therefore used in authentication and Active Directory security. A security principal account can be defined as a user account, group account, or computer account that is assigned a SID, and is also assigned permissions to access certain network resources or Active Directory objects, and to perform certain actions Read More
Implementing and Managing Group Policy Objects (GPOs)
On Overview on Group Policy Object (GPO) Implementation and the Group Policy Object Editor Group Policy settings are stored in a Group Policy Object (GPO). The types of Group Policy settings which can be stored in a GPO are listed below: Computer configuration settings are located in the Computer Configuration node. User configuration settings are located in the User Configuration node. A Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 computer has a local GPO. A local GPO exists only on that particular computer, and therefore only affects the computer on which Read More
Active Directory Management Tools
Active Directory or directory service management is a vital component of any administration process if Active Directory is implemented in the networking environment. The two types of management or administration methods that can be utilized to manage the directory service are: Administrative tools that utilize a graphical user interface (GUI). Command-line tools. Windows Server 2003 includes a number of new command-line tools that manage Active Directory objects as well as the various Active Directory directory parts. The Administrative tools that utilize a GUI can be accessed via the Administrative Tools Read More
Troubleshooting Group Policy
Through Group Policy, a wide variety of user and computer configuration settings can be applied to users and computers in Active Directory. If an Active Directory environment includes a hierarchy with many different organizational unit (OU) levels, when group policies are applied at these different levels within the hierarchy, it is almost certain that Group Policy behavior and settings will have to be troubleshooted. There are going to be situations when Group Policy settings produce an expected result. Group Policy settings are contained in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), which are Read More
The Global Catalog Server
The Global Catalog (GC) is an important component in Active Directory because it serves as the central information store of the Active Directory objects located in domains and forests. Because the GC maintains a list of the Active Directory objects in domains and forests without actually including all information on the objects and it is used when users search for Active Directory objects or for specific attributes of an object, the GC improves network performance and provides maximum accessibility to Active Directory objects. The Global Catalog server is the domain Read More
Configuring and Troubleshooting Active Directory Replication
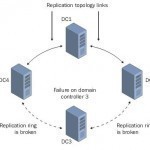
Active Directory is a distributed multimaster replicated database. All domain controllers host a full replica of the domain information for its own domain. Domain controllers in Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 environments hold a read/write copy of the Active Directory database. In these environments, changes can be made to the Active Directory database on any domain controller within the Active Directory environment. Replication is the process that ensures that changes made to a replica on one domain controller are transferred to replicas on the remainder of the domain controllers. Read More


Share on: