UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
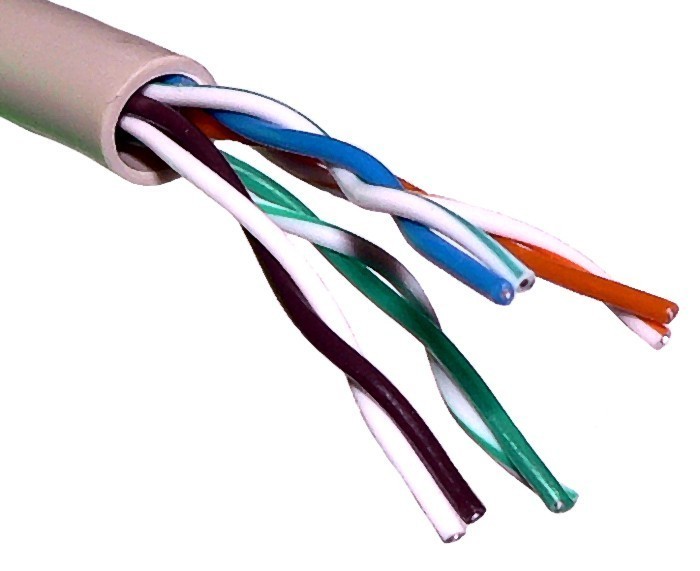
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) is a regular copper wire that joins many home and many business computers to the telephone company. UTP is the most common form of twisted pair wiring, because it is less expensive and easier to work with than STP (Shielded Twisted Pair). It is used in Ethernet 10Base-T and 100Base-T networks as well as in home and office telephone wiring.

Twisted pair is frequently linked with home usage. Whereas, an advanced grade of twisted pair is many a times used for horizontal wiring in LAN networks since it is less expensive than coaxial cable.
UTP Cable Standards
The following are a few UTP Cable standards used in the market:
Cat 3 UTP
Category 3 UTP is rated to carry data up to 10Mbit/s.
Cat 3 UTP was the standard cable used with Ethernet 10Base-T.
Cat 5 UTP
Category 5 UTP is rated to carry Ethernet up to 100Mbit/s and ATM up to 155Mbit/s.
Cat 5 UTP was the standard cable used with Ethernet 100Base-TX.
Cat 5e UTP
Category 5e UTP is an enhanced version of Cat 5 UTP.
Cat 5e UTP is rated to carry data up to 1000Mbit/s.
Cat 5e UTP is the standard cable used with Ethernet 1000Base-T.
Cat 5e can also be used to extend the distance of 100Base-TX cable runs up to 350 meters.
Cat 6 UTP
Category 6 UTP is very similar to Cat 5 UTP, except that it is designed and manufactured to even stricter standards.
UTP Termination
Two-pair (four-wire) UTP used for telephone use is normally terminated in an RJ-11 connector.
Four-pair (eight-wire) UTP used for data use is normally terminated in an RJ-45 connector.


Comments - 6 Responses to “UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.