Replication Topology is the route by which replication data travels throughout a network. Replication occurs between two domain controllers at a time. Over time, replication synchronizes information in Active Directory for an entire forest of domain controllers. To create a replication topology active directory must determine which domain controller's replicate data with other domain controllers. The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) is a built-in process that runs on each domain controller and regenerates the replication topology for all directory partitions that are contained on that domain controller. The KCC runs at Read More
ITIL Service Support

Like anything else, ITIL software is backed up by the ITIL Service Support. ITIL, or Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a system of software that has been approved by a standard of specifications under the authority of the British Office of Government Commerce. ITIL software generally falls under the category of customer service or system analysis. ITIL Service Support is used to help users with problems that they may experience with various ITIL software. In this article, we will go over and label the different parts of ITIL Service Support. Read More
How to Perform a DNS Lookup
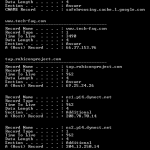
DNS, Domain Name System, is a complex hierarchical system which helps map Internet addresses with their respective machines over the World Wide Web. When a domain is created and hosted, a variety of information is linked with it. DNS Lookup is generally a process of digging out this related information for a specified domain name. This set of information could include pieces like domain availability, IP addresses, name servers, expiration date, registration/creation date, owner of the domain, etc. There are multiple ways to perform a DNS Lookup. Online Tools Many Read More
What is a Zeroconf?
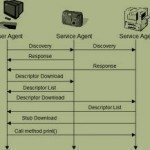
Zeroconf (zero configuration networking) refers to several protocols and techniques that are used together to create an IP (Internet Protocol) network with no special configuration servers or manual operator intervention. These networks allow novices to connect computers, network devices, scanners, and printers to create a functioning network without requiring manual configuration. Zeroconf does not require the user to set up Domain Name System services (DNS), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), or manually configure the computer’s network settings. The three primary technologies that comprise a zeroconf network are automatic resolution and Read More
Composite Video
A Composite Video is analog television signal's format before a sound signal is combined with it and modulated onto an RF carrier. It is the most common type of video interface that is used for receiving and sending an analog video signal to and from a television set. A CVBS (Composite Video with Burst and Sync) is usually used to designate a composite video and CVBS. Modulating the proper RF carrier frequency with composite video allows the composite video to be easily directed to any available broadcast channel. For most Read More
What is a Cutoff Frequency?
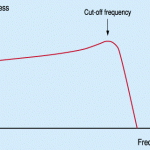
Cutoff frequency (corner or break frequency) is commonly used in the physics and electrical engineering fields. This frequency causes a device to stop operating in an efficient manner, resulting in it shutting down or being cut off. More technically, the cutoff frequency reduces energy flow through the device and prevents it from working as designed. That is to say, insufficient power prevents the device from operating efficiently. Cutoff Frequency Application Cutoff frequency is most commonly applied in the communications field. The phenomenon is found throughout many frequency ranges. If a Read More
How OnStar Works

OnStar was developed and deployed by General Motors for the purpose of providing fast and effective response in the event of vehicular accidents. OnStar has now been improved to provide more than the basic services. Now, it provides assistance with directions, car breakdown help as well as communications and leisure services. OnStar is a system for your automobile that performs many different functions, the most advertised being the fact that the company is alerted when you get in a car accident and they respond immediately by contacting you through the Read More
DFS (Distributed File System)
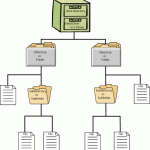
DFS (Distributed File System) provides a mechanism for administrators to create logical views of folders and files, regardless of where those files are physically located on the network. DFS also allows administrators to distribute shared folders and work loads across several servers for more efficient network and server resources use. Fault tolerance network storage resources are also available by using DFS. DFS is a service that provides a single point of reference and a logical tree structure for file system resources that may be physically located anywhere on the network. Read More
Auger Electron Spectroscopy
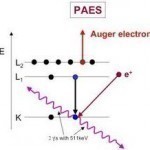
Pierre Auger discovered the Auger effect with x-rays that were involved in simultaneous cloud chamber usage. Auger observed that excited atoms emitted energetic electrons when the atoms relaxed. When the Auger effect was first discovered, it served little to the scientific community and was not utilized until the 1950s. The effect was then used to help improve the experimentation of chemical/compositional surface environments, in metallurgy, and in microelectronics. How Auger Electron Spectroscopy Works Auger Electron Spectroscopy is when specialized equipment that can test samples of materials is used to measure Read More
Point-to-Point Protocol
The Point-to-Point protocol (PPP) originally emerged as an encapsulation protocol for transporting IP traffic over point-to-point links. PPP also established a standard for the assignment and management of IP address, synchronous (start/stop) and bit-oriented synchronous encapsulation, network protocol multiplexing, link configuration, link quality testing, error detection, and option negotiation for such capabilities as network layer address negotiation and data compression negotiation. PPP supports these functions by providing an extensible Link Control Program (LCP) and a family of Network Control Program (NCP) to negotiate optional configuration parameters and facilities. In addition Read More


Share on: