What is a PID Controller?
A PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) controller is a device that makes changes to a system based on current and intended settings. PID controllers are used in a wide variety of industrial control systems and are the most commonly used feedback controllers in the world. PID controllers allow users to obtain and/or maintain preferred conditions within a system by modifying a variable input until preferred conditions are reached.
How a PID Controller Works
PID controllers rely on three main elements: the process variable, the setpoint, and the manipulated variable. The process variable refers to the system’s current condition. For example, in a hot water system, the process variable would be how hot the water currently is. The setpoint refers to the system’s intended conditions. For example, the setpoint is how hot or cold a user wishes the water to be. The manipulated variable refers to the actual mechanism that allows the system to change its conditions. For example, the manipulated variable is the valve that allows the hot water system to adjust how much hot water is allowed to flow into the tap. When a user adjusts the temperature of the water, the system compares what the current water temperature is and the intended water temperature that the user sets and calculates the difference between the two. The system then moves the valve accordingly to increase or decrease the hot water level in the tap.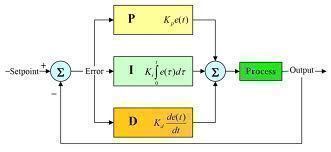
Applications
PID controllers are used in a variety of devices and equipment, most of which are automated and do not require any complex processes. They are used in water purification systems along with other sensors in order to alter the level of solvents and other chemicals in the water as well as control mechanisms that transport the water from one area of the facility to another. PID controllers are also used in signal modulation for digital devices to measure varying voltages.
Disadvantages
Although PID controllers are the most widely used control mechanism in the world, they are also the most basic. Therefore, PID controllers are significantly limited in their capabilities, especially when complex processes are required to perform a task. PID controllers are only capable of measuring varying inputs and calculating the difference between them. Because of this, some subject specific industries must use larger and/or more expensive controllers.


Comments - No Responses to “What is a PID Controller?”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.