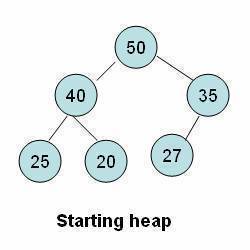
Insertion of an Element in a Heap
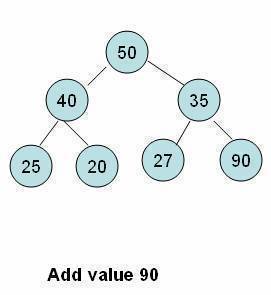
- An element is initially inserted as the last child of the heap.
- On insertion, the heap remains a complete binary tree, but the order property may be violated.
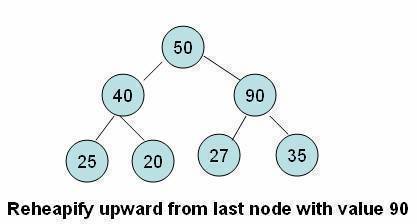
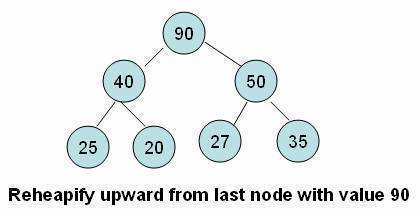
- We have to perform a series of operations to move the element up from the last position until either it ends up in a position where the order property is satisfied or we hit the root node.
- In this tutorial, we refer to this process as the reheapify upward operation.
Algorithm
ReheapifyUpward(heap,start)
Here heap is a linear array and start is the index of the element from where the reheapifyupward operation is to start. It uses parent as the index of the parent node in the heap.
Begin if heap[start] is not root node then if (heap[parent]<heap[start]) then swap heap[parent] and heap[start] call ReheapifyUpward(heap,parent) endif endif end
C/C++ implementation
.cf { font-family: Lucida Console; font-size: 9pt; color: black; background: white; } .cl { margin: 0px; } .cb1 { color: green; } .cb2 { color: blue; }
void reheapifyUpward(int heap[],int start)
{
int temp, parent;
if(start>1)
{
parent=start/2;
if(heap[parent]<heap[start])
{
temp = heap[start];
heap[start] = heap[parent];
heap[parent] = temp;
reheapifyUpward(heap,parent);
}
}
}


Comments - No Responses to “Insertion of an Element in a Heap”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.