What is a Biometric Coprocessor?
A biometric coprocessor is a device that is capable of scanning a user’s physical attributes in order to allow access to a building or computer network. A biometric coprocessor is essentially a fingerprint reader, but may also include sensors that analyze the user’s eyes, voice, or even breath. The term “biometric coprocessor” comes from the word “biometric” – the measurement of biological attributes, and “coprocessor” – a computer system that can keep track of several tasks at the same time.
How Does A Biometric Coprocessor Work?
A biometric coprocessor scans the user’s physical attributes and then compares what it detects with a similar sample that is stored on an internal hard drive. If there is a match, the computer allows the user to access the building or computer system that it is protecting. Biometric coprocessors can use lasers, cameras, heartbeat sensors, and other input devices to gauge the user’s physical attributes.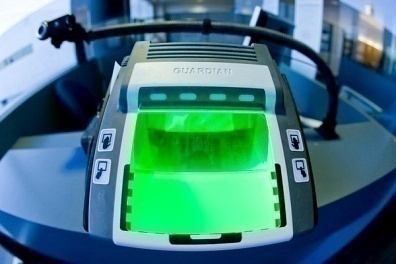
Applications
Biometric coprocessors have become more common in recent years, with fingerprint readers being introduced for domestic computers, cell phones, media players, and similar electronic devices in order to ensure that only the device’s owner has access to it. Biometric coprocessors are also used in ATMs, most high-security buildings, and in some industrial machinery. They have even been put in cars in order to gauge the driver’s blood/alcohol level, heartbeat, respiratory rate, and other physical conditions before the driver is allowed to start the engine. Biometric coprocessors are also used in the medical industry to measure the health of patients and can also be used for general security purposes in order to detect criminals and those whose reactions fall outside the normal range of human reactions.
Advantages
Biometric coprocessors have several advantages. They are capable of actually scanning the user’s physical attributes, instead of relying on security guards and other personnel to accurately decide who they give access. Biometric coprocessors are often compact, lightweight, and relatively inexpensive compared to other security systems. Biometric scanners compare a series of physical attributes with stored samples, so they are highly reliable and efficient at making proper security-related decisions.
Disadvantages
Biometric coprocessors have several disadvantages. Physical attributes can change over long periods of time and confuse biometric coprocessors that are used on a daily basis. Additionally, some systems become dependent on biometric coprocessors and cannot function properly without them.


Comments - No Responses to “What is a Biometric Coprocessor?”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.