Active Directory Authentication Types
The two types of authentication are Mutual Authentication and NTLM. Mutual Authentication requires both the server and the client to identify them. NTLM only requires the client to be validated by the server.
Two types of authentication are Mutual Authentication and NTLM Authentication.
Mutual Authentication
Mutual Authentication is a security feature in which a client process must prove its identity to a server, and the server must prove its identity to the client, before any application traffic is sent over the client-to-server connection. Identity can be proved through a trusted third party and use shared secrets, as in Kerberos v5, or through cryptographic means, as with a public key infrastructure.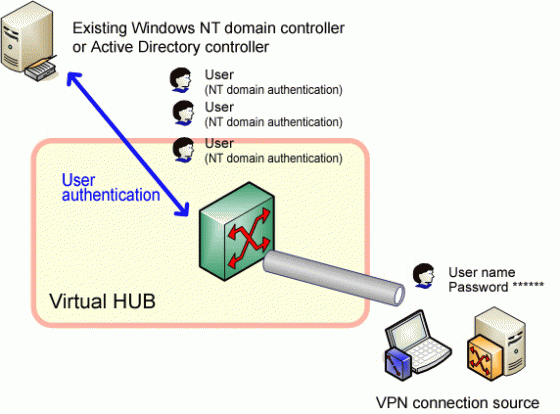
Support for mutual authentication is provided by the security support provider interface (SSPI) and is exposed directly through the SSPI APIs and services that layer upon SSPI, including RPC and COM+.
Not all security packages available to SSPI, or all services running Windows 2000 or later, support mutual authentication. An application must request mutual authentication and a supporting security package to obtain mutual authentication.
NTLM
NTLM authentication supports three methods of challenge/response authentication:
- LAN Manager (LM)
This is the least secure form of challenge/response authentication. It is available so that computers running Windows 2000 or later can connect in share level security mode to file shares on computers running Microsoft Windows for Workgroups, Windows 95, or Windows 98. - NTLM version 1
This is more secure than LM challenge/response authentication. It is available so that clients running Windows 2000 or later can connect to servers in a Windows NT domain that has at least one domain controller that is running Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 or earlier. - NTLM version 2
This is the most secure form of challenge/response authentication. It is used when clients running Windows 2000 or later connect to servers in a Windows NT domain where all domain controllers have been upgraded to Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 4 or later. It is also used when clients running Windows 2000 or later connect to servers running Windows NT in a Active Directory domain.


Comments - No Responses to “Active Directory Authentication Types”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.