Amino Acids
An amino acid is a molecule that contains three specific components. The first is an amine group which contains a nitrogen and two hydrogen. The second component is a carboxylic acid which is a weak acid which is written as COOH. Sometimes, it is written as R-COOH to document that the carbon is attached to some other side chain. The side chain, therefore, is the third component of an amino acid and the side chain differs from amino acid to amino acid.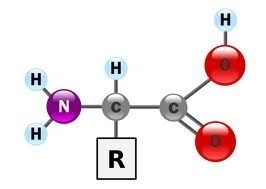
The Twenty One Amino Acids
There are twenty one amino acids in the human system. Each of these amino acids contains the carboxylic acid and the amine–in some form–but has a differing side chain. They each have their own name, a three letter abbreviation and a single letter abbreviation. The amino acids are:
| Amino Acid |
Three Letter Abbreviation |
One Letter Abbreviation |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Aspartic Acid | Asp | D |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamic Acid | Glu | E |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |
| Selenocysteine | Sec | U |
The selenocysteine and a 22nd amino acid, Pyrrolysine–three letter is Pyl and one letter is O–are both incorporated by overriding stop codons, so they are carefully categorized.
Need for Amino Acids
The amino acid is incredibly important to life. It has many functions in metabolism that, without, would make living impossible. To begin with, amino acids act as the building blocks of proteins. What this means is that a protein is just a linear chain of amino acids. However, this linear chain, to ensure that the large macromolecules are able to fit within cells, fold over each other forming much tighter shapes. This leads to the definition of proteins. They are chemically defined by the order of the amino acid, their primary structure which leads to their secondary structure. Following this comes their tertiary structure which is the shape of the protein and then the quaternary structure if there are many proteins grouped.
In other cases, when the protein is broken apart for energy–through a biochemical reaction known as oxidation–two things are created: urea and carbon dioxide. When the protein is broken, the amino group is removed and fed into the urea cycle. The other half is a keto acid which enters into the citric acid cycle. This is what creates energy.
Amino acids are the building blocks of the human body. While DNA carries the genetic code and the RNA carries the template for the amino acid, it is the amino acid itself that, when combined with other amino acids, that make up the proteins that make our bodies. Therefore, amino acids are incredibly important to life.


Comments - No Responses to “Amino Acids”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.