High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection, also known as HDCP, is a newer form of Digital Rights Management (DRM) that was designed to control digital video and audio content. The technology was originally created by Intel to ensure that digital audio and video travelling across a Digital Video Interface (DVI) or High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) would follow the various guidelines put forth by the Digital Content Protection group. What Is Required Of An HDCP Capable Device In order for a product to claim that it is HDCP capable, it must have a Read More
1080p vs. 1080i

Most TV buyers are looking for the highest quality picture possible. For those shopping for a TV there is a controversy brewing about which is better 1080p or 1080i. However, the truth of the matter is that for most people both of these formats will deliver the same quality picture. Here is why. 1080i and 1080p Both 1080i and 1080p deliver the same pixel resolution. The resolution is 1,920 pixels across the display screen by 1,080 pixels down the display screen. Since both formats offer the same resolution, the only Read More
DBS (Direct Broadcast Satellite)

A DBS, or Direct Broadcast Satellite, is a type of satellite that is used to broadcast data directly to a residence or commercial office, without the use of intermediary cables or other routing equipment. DBS systems are most commonly used for direct broadcast television and Internet access, in which users from anywhere in the world can receive television and Internet services even if no local cable companies are available. Because DBS systems are able to transfer data directly to and from a residence or other property without the use of Read More
VideoGuard
VideoGuard is an encryption method that NDS produced. It is used for conditional broadcasting services such as broadband television and the Internet. Since satellites, radio towers, and all other broadcasting equipment broadcast signals without discretion to which subscribers receive them, VideoGuard is necessary in order to distinguish which television channels, Internet features, and other services subscribers are able to receive. How VideoGuard Works Since broadcasting systems broadcast the same signals to everyone, VideoGuard encryption must be built directly into the programming of the set-top box that is connected to the television. Read More
What is a Cutoff Frequency?
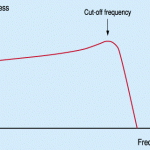
Cutoff frequency (corner or break frequency) is commonly used in the physics and electrical engineering fields. This frequency causes a device to stop operating in an efficient manner, resulting in it shutting down or being cut off. More technically, the cutoff frequency reduces energy flow through the device and prevents it from working as designed. That is to say, insufficient power prevents the device from operating efficiently. Cutoff Frequency Application Cutoff frequency is most commonly applied in the communications field. The phenomenon is found throughout many frequency ranges. If a Read More
Picture Sharpness
Picture sharpness can be summed up by being defined as the fine details found in an image. Images can be analog, such as a photograph or on a standard TV screen. They can also be digital made out of pixels or small bits of information as in HDTV (high definition TV) or digital photo images. When a picture has lots of fine details, it is said to have good contrast. Contrast is an integral part of picture sharpness, it can be said it is the differentiating information within an image Read More
How Does Satellite TV Work?

Satellite TV works by broadcasting video and audio signals from geostationary satellites to satellite dishes on the Earth’s surface. These geostationary satellites orbit the earth in a region of space known as the Clarke Belt, which is approximately 22,300 miles above the equator. Each of these satellites carries a number of transponders. These transponders each carry a signal back to the Earth. These signals are typically on C Band, Ku Band, or Ka Band. The band of a signal describes, in broad terms, the frequency of the signal. After travelling Read More
Ultra HD
Ultra HD (Ultra High Definition), also called UHDV (Ultra High Definition Video) and Super Hi-Vision, is a digital video format proposed by the Japanese research group and broadcasting company, NHK Science and Technical Research Laboratories. Ultra HD is a giant leap forward from HDTV. It provides a video resolution that contains 16 times more pixels than a conventional HDTV. That is, against 1,080 lines of resolution of HDTV, Ultra HD offers 4,320. More precisely, Ultra HD provides 7,680 x 4,320 pixels in a widescreen aspect ratio of 16×9, for a Read More
How to Download a Video from a Camcorder to a Computer

The process of downloading a video from a camcorder to a computer depends on whether the camcorder is digital or analog (old-style camcorder that uses tapes). For an analog camcorder, install a signal digitizer card in the computer, which is fairly common with today’s readily available off-the-shelf TV tuner cards. This card converts the analog camcorder signal to a digital one, and can be purchases for under $100. However, try to bear in mind the availability of space on the hard drive, due to the fact that even short video Read More
MediaGuard

MediaGuard is a conditional access system used by television broadcasters such as the Canal+ Group, Orbit, Malaysia’s Astro, and China’s BGCTV. MediaGuard is a product of Nagra France. Nagra France is a division of the Kudelski Group, a Swiss company. The Kudelski Group also owns Nagravision. MediaGuard competitors include Conax, CoreTrust, Cryptoworks, Irdeto Access, Latens, SafeAccess, Verimatrix, Viaccess, VideoGuard, and Nagravision.


Share on: