A frequency changer makes it possible to change electricity moving at one frequency to another frequency. However, in order to fully understand what a frequency changer does, it is helpful to understand the frequency of electricity. The Frequency of Electricity Electricity doesn't move at one specific speed. In fact, it can move at many speeds. Some electronic devices require a set frequency or speed, while others can run proficiently at a range of speeds. The speed of electricity or frequency is measured in Hertz or Hz. One Hertz is one Read More
Attic Antennas

An attic antenna is one that is mounted inside of an attic in order to provide maximum range as well as protection from rain, snow, sun, wind, and animals. Attic antennas are rather common and provide quality reception for those who live in rural areas, away from most radio transmitters. While attic antennas do not have as good a reception as outdoor antennas, they are covered and do not detract from the home’s appearance. How Attic Antennas Work Except that they are mounted indoors, attic antennas use the same principles Read More
Types of Projector Lamps

A projector lamp is used to transfer an image from a multimedia projector onto a larger screen. Earlier halogen bulbs were used for many years for projection purposes, but were discontinued as halogen produced a yellow tone on the images. A projector lamp relies on an intense light bulb, called a metal halide bulb, to produce a brilliant white light. The light bulb shines onto a number of small mirrors inside the machine and transfers the image through the air and onto the screen. These machines can project slides, films, Read More
Metal Detector
A metal detector uses an electromagnetic field to detect the presence of a concealed metal object. The range depends on the strength of the field, and is usually less than one meter from the search head. The three detection methods are beat frequency oscillation, very low frequency, and pulse induction. Metal detectors were first introduced around 1930 and are used in many different applications. How Metal Detectors Work The beat frequency oscillation method uses two coils connected to an oscillator. When the search head coil passes over a metal object, Read More
Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is a device that automatically breaks an electrical circuit whenever the circuit becomes overloaded or an unintentional short circuit occurs. Circuit breakers have a set electric current load capacity which when breached results to automatic circuit shutdown. Overloading occurs whenever the wires comprising an electrical circuit are forced to carry and conduct an electric charge beyond their capacity. Whenever this happens, the wires heat up. This may result in insulation breakdown (in which a short circuit may occur) or an electrical fire. An unintentional short circuit occurs Read More
Mobile Satellite Service

Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) is a type of mobile telephone service that depends on portable terrestrial satellites rather than fixed terrestrial satellites that are also known as cell phone towers. Portable terrestrial satellites are similar to cell phone towers, but can be mounted on moving vehicles such as cars, ships, and airplanes, and individual users can even carry them. Mobile Satellite Service is not as common as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications), but is frequently used for its global reception. How Mobile Satellite Service Works Mobile Satellite Service Read More
Motes

Motes are also sometimes referred to as smart dust. One mote is composed of a small, low powered and cheap computer connected to several sensors and a radio transmitter capable of forming adhoc networks. The computer monitors the different sensors in a mote. These sensors can measure light, acceleration, position, stress, pressure, humidity, sound, and vibration among others. Data gathered are passed on to the radio link for transmission from mote to mote until data reaches the transmission node. These radio links between motes have a transmission distance of 10-200 Read More
Spot Beam
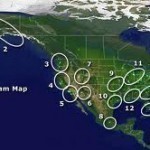
A spot beam is a beam of radio signals that is directed towards a specific area on the Earth’s surface. Spot beams are the opposite of broad beams, which are beams that are directed towards a large area of the Earth’s surface. While broad beams are used for general telecommunication and surveillance, spot beams are used for magnified views of the Earth and are ideal for targeting purposes and close-up surveillance of specific areas. Spot beams are also used in telecommunications for direct links between a specific satellite and a Read More
Voltage Drop
Voltage is the measurement for the electrical force between two points that drives the current. More specifically, voltage is the measure of the energy per unit charge that is equal to the electrical potential difference between two measured points. Volts are normally measured by a voltmeter. Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage in an electrical circuit between the source of power and the load on a circuit. Many electrical codes throughout the United States and the developed world set specific guidelines for the maximum voltage drop permitted in an Read More
Coulomb
The coulomb is the standard unit of electric charge. One coulomb is defined as the amount of charge carried by one ampere of current in one second. One coulomb can also be defined as the amount of charge needed to create one volt of potential difference in a one farad capacitor. The symbol for the coulomb is an uppercase C. History of the Coulomb The coulomb was defined at an international conference in 1881, and is named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (1736-1806), a French physicist. He discovered Coulomb’s law which Read More


Share on: