An IDU, or In-Door Unit, is a telecommunication device that is used in satellite television and Internet service to receive and decode satellite transmissions. An IDU is a box that connects to the user’s television and/or router and contains a built-in satellite receiver that may also be connected to a satellite dish on the roof or exterior wall of the user’s home. An IDU is responsible for receiving the satellite signals broadcasted by the user’s satellite service provider and decoding them in order to provide the user with satellite television Read More
ODU (Out-Door Unit)

ODU (Out-Door Unit) refers to the set of satellite equipment which is placed outside of the building. The ODU typically includes a satellite dish, a feedhorn, and a LNB (Low Noise Block). In bi-directional satellite systems, the ODU will also include a BUC (Block Up Convertor). The ODU is connected to the IDU (In-Door-Unit) by the IFL (Inter-Facility-Link). The dish receives the signal and focuses it on the feedhorn. The feedhorn delivers the signal to the LNB. The LNB converts the satellite frequencies to an Intermediate Frequency (IF) which is Read More
Geostationary Satellite
Geostationary satellites are located exactly above the earth’s equator and revolve around the earth in a circular orbit. Their revolving speed and direction (west to east) are exactly same as that of the earth, which makes it look stationary from the earth’s surface. The exact altitude of these satellites above the equator is approximately 36,000 Kilometers (22369 Miles). A geostationary satellite has to be at a set distance above the earth or it will suffer altitude decay. If it is too far from the Earth, it will escape the Earth’s gravitation Read More
QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying)
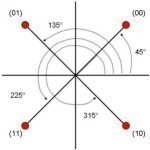
QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) is a phase modulation algorithm. Phase modulation is a frequency modulation version where the carrier wave’s phase is modulated to encode bits of digital information in each phase change. The “PSK” in QPSK refers to the use of Phased Shift Keying. Phased Shift Keying is a form of phase modulation that is accomplished by using a discrete number of states. QPSK refers to PSK with 4 states. With half that number of states, there is a BPSK (Binary Phased Shift Keying). With twice the number Read More
Low Earth Orbit
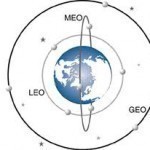
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) refers to a satellite which orbits the earth at altitudes between (very roughly) 200 miles and 930 miles. Low Earth Orbit satellites must travel very quickly to resist the pull of gravity — approximately 17,000 miles per hour. Because of this, Lowe Earth Orbit satellies can orbit the planet in as little as 90 minutes. Low Earth Orbit satellite systems require several dozen satellites to provide coverage of the entire planet. Low Earth Orbit satellites typically operate in polar orbits. Low Earth Orbit satellites are used Read More
Transponder

A transponder is an automatic electronic monitoring or control device that receives, cross-examines, amplifies and retransmits the arriving signal. It is primarily implemented in wireless communication. The word ‘Transponder’ itself is a combination of two words; transmitter and responder (occasionally abbreviated to TPDR, TR, XPNDR, and XPDR). A transponder works by receiving a signal on a component called “interrogator” since it effectively inquires for information, then automatically transmitting a radio wave signal at a predestined frequency. In order to broadcast a signal on a dissimilar frequency than the one received, Read More
Mobile Satellite Service

Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) is a type of mobile telephone service that depends on portable terrestrial satellites rather than fixed terrestrial satellites that are also known as cell phone towers. Portable terrestrial satellites are similar to cell phone towers, but can be mounted on moving vehicles such as cars, ships, and airplanes, and individual users can even carry them. Mobile Satellite Service is not as common as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications), but is frequently used for its global reception. How Mobile Satellite Service Works Mobile Satellite Service Read More
Spot Beam
A spot beam is a beam of radio signals that is directed towards a specific area on the Earth’s surface. Spot beams are the opposite of broad beams, which are beams that are directed towards a large area of the Earth’s surface. While broad beams are used for general telecommunication and surveillance, spot beams are used for magnified views of the Earth and are ideal for targeting purposes and close-up surveillance of specific areas. Spot beams are also used in telecommunications for direct links between a specific satellite and a Read More
Where to See Free Satellite Images

Satellite images were initially the exclusive realm of military and government agencies. They then became commercially available at very steep prices. Technology has now improved to the point where satellite images are available so inexpensively that they are now provided for free online. Free Satellite Images on the Web The best and by far the most popular source of web based free satellite images is Google Maps. This product can be directly used from the web browser. In addition to the pure satellite view, Google Maps lets users choose a Read More
PSK (Phased Shift Keying)
Digital modulation is no new concept. Programmers and people working in today’s technological field know it for sure, as they have been using certain modulation techniques to transmit data digitally. However, several techniques are available for techies to choose from, and out of three popular digital modulation options, the PSK or Phase Shift Keying tops the list of the most valuable. PSK, as it is commonly known, works to modulate or adjust certain parts of the reference signal, which essentially is the carrier wave. This signal is changed in response Read More


Share on: