H.323
H.323 is an ITU standard multimedia conferencing protocol, which includes voice, video, and data conferencing, for use over packet-switched networks.
H.323 was the first standard for VoIP, but is being supplanted by SIP.
H.323 defines five components of a multimedia network:
- Terminals
- Multipoint Control Units (MCUs)
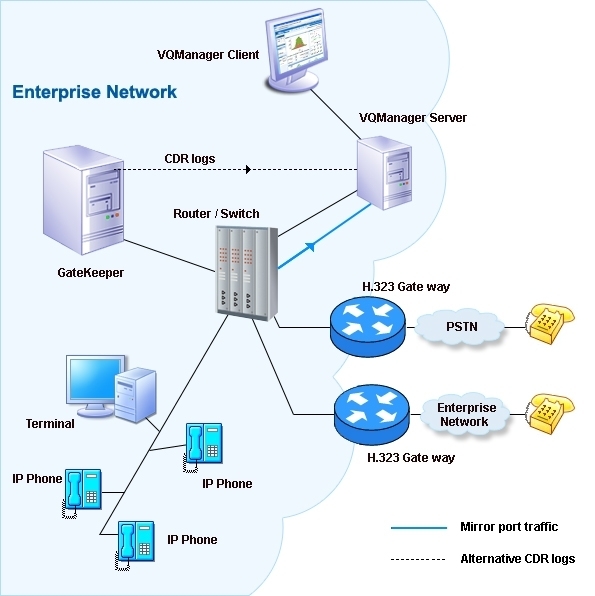
- Gateways
- Gatekeeper
- Border Elements
Terminals are telephone and PC equipment which connect end-users to the H.323 network.
MCUs are responsible for managing conferences. MCU’s consist of a Multipoint Controller (MC) and an optional Multipoint Processor (MP). The MC manages signaling and the MP manages media mixing and switching.
Gateways interface the H.323 network with other networks, including PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) and other H.323 networks. Gateways consist of a Media Gateway Controller (MGC) and a Media Gateway (MG). The MGC is is responsible for call signaling functions and the MG is responsible for media-related functions.
Gatekeepers are responsible for admission control and address resolution. Gatekeepers are able to provide advanced services such as normally found in PBX’s.
Border Elements are positioned between two H.323 networks and assist in call routing and call authorization.


Comments - No Responses to “H.323”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.