DDR3 SDRAM (Double Data Rate Three Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) is the third generation of DDR SDRAM. DDR3 SDRAM improves on DDR2 SDRAM in several significant ways: Higher bandwidth due to increased clock rate Reduced power consumption due to 90mm fabrication technology Pre-fetch buffer is doubled to 8 bits to further increase performance The voltage of DDR3 SDRAM DIMMs was lowered from 1.8V to 1.5V. This reduces power consumption and heat generation, as well as enabling more dense memory configurations for higher capacities. Standard DDR3 SDRAM DIMM's DDR3 SDRAM Read More
Registered Memory

Registered memory modules have built-in registers on their address and control lines. A register is a very small temporary holding area (usually 64 bits) for data. These registers act as buffers between the CPU and the memory. The use of registered memory increases system reliability, but also slows the system down a very slight bit as data must be moved through the registers. Some systems do not support registered memory, others require registered memory, and many more give you the option to use registered or unregistered memory. The use of Read More
ROM (Read Only Memory)
Read-Only Memory or ROM is an integrated-circuit memory chip that contains configuration data. ROM is commonly called firmware because its programming is fully embedded into the ROM chip. As such, ROM is a hardware and software in one. Because data is fully incorporated at the ROM chip's manufacture, data stored can neither be erased nor replaced. This means permanent and secure data storage. However, if a mistake is made in manufacture, a ROM chip becomes unusable. The most expensive stage of ROM manufacture, therefore, is creating the template. If a Read More
SODIMM

A SODIMM (Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module) is a series of small DIMM chips that is specifically designed to fit into smaller working environments such as mobile devices and notebook computers. SODIMMs are designed to be smaller than regular DIMMs due to space restrictions, but provide the same processing capabilities. Both SODIMMs and regular DIMMs are simply a collection of RAM chips that provide memory management functions to personal computers, servers, and other workstations. How SODIMM Works SODIMM provides memory management to the small processors found in mobile Read More
DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM, an abbreviation for double data rate two synchronous dynamic random access memory, is a type of a random access memory (RAM) commonly used in personal computers and various digital electronics today. This offspring from the SDRAM (synchronous dynamic random access memory), a part of DRAM (dynamic random access memory), is like an evolution from the DDR SDRAM; it can operate the external data bus twice as fast as its predecessor. This was possible by abandoning the original clock rate of the DDR, and operating the memory cells at Read More
DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module)

Dual Inline Memory Module or DIMM is a series of Random Access Memory (RAM) chips mounted on a small printed circuit board. The entire circuit collectively forms a memory module. DIMMs are commonly used in personal computers, servers, and high-end workstations. The DIMM makes physical contact with the computer’s data bus through teeth like connectors that fit into a socket on the mother board. The earlier memory modules were known as SIMMs or Single Inline Memory Modules and had a 32-bit data path. DIMMs on the other hand use a Read More
SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity)
SDHC stands for Secure Digital High Capacity. It is a format for new memory cards that is based on the 2.00 specification of the SDA (Secure Digital Association).The name Secure Digital is due to their ability to protect copyright, using digital copyright management. This has made these memory cards a favorite choice in the audiovisual industry. These flash memory cards are available in various capacities, the minimum being 4 GB. SDHC cards are removable and are used in compatible digital devices like MP3 players, camcorders, camera phones, etc. Why SDHC? Read More
MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random-Access Memory)
MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory) is being considered as a viable replacement for current DRAM technology. Its key difference to the latter is its use of magnetic fields to save memory bits which makes the memory "permanent." As such, MRAM technology allows for faster access and data security. Current RAM Technology Current RAM technology uses an electrical charge to store memory bits. Microminiaturized capacitors and transistors in an integrated circuit are 'stacked up' to create high-density, large-memory but physically small chips. A typical memory chip stores up to 1 Gb Read More
What is a Hypervisor?
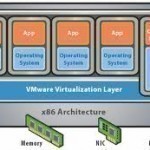
A hypervisor is a virtualization technique that runs multiple operating systems on the device. While non-hypervisor virtualization techniques run multiple operating systems on domestic computers and hand-held devices, hypervisors are used exclusively on devices whose sole task is to run multiple guest operating systems for commercial or industrial purposes. Hypervisors are used in gaming technologies, commercial servers, and malware systems. They are effective at reducing system requirements by running simultaneous virtual systems on the same hardware and sharing that hardware’s resources. How Hypervisors Work Hypervisors mimic operating systems by running Read More
DDR SDRAM
DDR SDRAM is Double Data Rate SDRAM. DDR SDRAM is an improvement over regular SDRAM, also known as SDR SDRAM (Single Data Rate SDRAM). DDR SDRAM doubles the bandwidth of SDR DRAM by transferring data twice per cycle on both edges of the clock signal, implementing burst mode data transfer. DDR SDRAM is being supplanted by DDR2 SDRAM. Standard DDR SDRAM DIMM's DDR SDRAM is normally packaged in DIMM modules. DIMM Module Chip Type Clock Speed Data Rate Transfer Rate PC1600 DDR200 100 200 1,600 PC2100 DDR266 133 266 2,133 Read More


Share on: