DISCLAIMER: This is a one way process and all steps must be taken to ensure that data is backed up before attempting. The author is in no way responsible for loss of data or damage to disk, data, and the computer as a whole. Before beginning, become familiar with the following terms : FAT : File Allocation Table is a computer file system architecture that Bill Gates and Marc McDonald developed in the late 1960s and 1970s. It is the main file system in use for MS-DOS and the earlier Read More
What is a CDFS?

The term CDFS (CD File System) is used for both the Linux and Windows Operating Systems (OSs). CDFS is a file system that was created for Linux in 1999 and exports all boot images and tracks on a CD as normal files. On the Windows OS, CDFS is the driver file that is used to support CD-ROM players and replace the traditional MSCDEX driver used on MS-DOS. CDFS also uses a VCACHE driver to control CD-ROM caches on Windows computers, which makes music playback smoother. CDFS Commands on Linux CDFS Read More
The File Allocation Table (FAT) File Systems

Understanding the FAT File Systems The FAT file system was initially introduced with the MS-DOS operating system (OS) when hard disks were generally much smaller, and the structure of folders was not as intricate as it is in networks today. The FAT file system continues to be supported by each Microsoft OS since its advent. The initial FAT file system could only support a maximum partition size of 2GB. What this meant was that where a computer’s hard disk drive was greater than 2GB, you had to partition the drive Read More
What is a GPT Protective Partition?
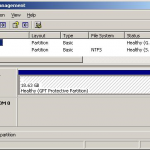
A GPT protective partition is a partition on a hard drive that a GUID Partition Table protects. A partition is a continuous area of storage space on a hard drive that is separated from the rest of the hard drive and acts as its own storage device. A GPT protective partition cannot be deleted or reformatted, but can be much larger than partitions that the Master Boot Records (MBR) generate. GPT protective partitions arise from creating partitions on a hard drive that GPT manages. While GPT protective partitions are useful Read More
What Are Dynamic Disks?
What are Dynamic Disks A dynamic disk refers to a hard drive that can be altered at any time to include additional partitions or volumes. This differs from basic disks that only include standard and extended partitions that are setup when the disk is first formatted. Dynamic disks can handle all of the following volumes. Simple Volumes A simple volume refers to the standard volume in which computers often work with. A simple volume is basically a folder on a hard drive that holds all of the user's information. For Read More
How to Configure NTFS Quotas
Use disk quotas to manage storage growth in distributed environments. Disk quotas allow you to allocate available disk space to users based on the files and folders that they own. Windows 2003 disk quotas track and control disk space usage on a per-user, per-partition basis. Characteristics of Windows 2003 Server Disk Quotas Disk usage is based on file and folder ownership. When a user copies or saves a new file to an NTFS partition or takes ownership of a file on an NTFS partition, windows 2003 changes the disk space Read More
NTFS File Compression
One feature available when you format a volume with the NTFS file system is file compression. NTFS compression can only be applied to a partition or volume that is formatted with the NTFS file system. Through NTFS, you can create additional storage space for files by compressing either single files, or all files in a NTFS folder. Files in a compressed folder are compressed when folder compression is enabled. Any subfolders included in the compressed folder can also be compressed. You can also compress all files on NTFS volumes. A Read More
NTFS Permissions
An Overview of NTFS In order to store data on a local partition on a Windows server, you have to format it with a file system. The system that you use influences the manner in which data is stored on the disk. It also specifies the security that can be defined for folders and files stored on the partitions. Although Windows servers offer support for the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system, NT file system (NTFS), and CDFS (Compact Disc File System), the file systems generally utilized by local partitions Read More
Understanding Volume Shadow Copies
Volume Shadow Copies Overview Volume shadow copies, a new Windows Server 2003 feature, are used to create copies of files at a specific point in time, or set time interval. Shadow copies can only be created on NTFS volumes to create automatic backups of files or data per volume. When enabled, the Shadow copies feature protects you from accidentally losing important files in a network share. Remember that when users delete files from over the network, those files are permanently deleted. Because shadow copies enable users to view previous versions Read More
ExFAT
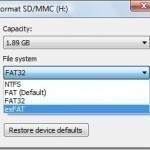
The Microsoft Corporation in conjunction with Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1) released the exFAT file system. The exFAT file system was produced in order to address the short comings of the FAT32 file system; specifically on portable media such as USB sticks or portable hard drives where NTFS file structure use is inappropriate. The exFAT file system is also referred to as FAT64 in some circles. The Microsoft Corporation has a patent pending, which will require licensing for the use of the format. The exFAT structure is supported on Read More


Share on: