A protocol is a collection of specifications or rules for data packets that enable information to be sent over the network. Network protocols are designed for network communication. In order to understand the different protocols available and their efficiencies, lets first look at the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. This is the standard model for network communication developed by International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The design of the OSI model is that of a stack of protocols. The different stacks of protocols operate together to transport data and enable Read More
APIPA
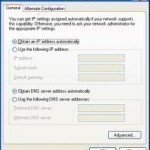
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) Overview DHCP is a service that functions at the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack. One of the primary tasks of the DHCP service is to automatically assign IP addresses to DHCP clients. A server running the DHCP service is called a DHCP server. The DHCP service automates the configuration of TCP/IP clients because IP addressing occurs through the system. The DHCP server assigns IP addresses from a predetermined IP address range(s), called a scope. To summarize, the DHCP server dynamically assigns IP addresses Read More
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
An Overview on Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol was developed by Netscape Communications, and enables secure communication over the Internet. SSL works at the transport layer of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which makes the protocol independent of the application layer protocol functioning on top of it. SSL is an open standard protocol and is supported by a range of both servers and clients. SSL can be utilized for the following: Encrypt Web traffic using Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). When HTTP is utilized together with Read More
The Windows Routing Table
When routers need to forward packets, they interpret the packets’ addresses then use the information in the routing tables to pass the packet on. Data packets contain both source and destination addresses in their packet headers. This is the information that is used when routing decisions need to be made. The destination address is compared with the local address to determine the following information on how to route the packet: Should the packet be sent up the stack on the local host? Should the packet be sent to a different Read More
How to Set a Static IP Address in Windows
Setting up a static IP address on a computer network can be very helpful, especially if port forwarding is required on the network. A static IP address makes it possible for a port configuration to work, but since dynamic IPs create a new IP address each time a computer starts up, port forwarding on a network can become inoperable. Before tips on how to set up a static IP address are discussed, here is some information regarding IPs in general. What is an IP Address? Internet Protocol (IP) address is Read More
Installing and Configuring TCP/IP
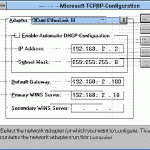
Installing TCP/IP TCP/IP is installed automatically when the Windows Server 2003 setup process runs. It is not usually necessary to install TCP/IP after the Windows Server 2003 setup process completed. The instances when you might need to manually install TCP/IP are listed below: TCP/IP was disabled when the Windows Server 2003 setup process executed. TCP/IP was uninstalled from the computer. How to install the TCP/IP protocol suite Click Start, Control Panel, and then click Network Connections In the Network Connections window, right-click the network connection for which you want to Read More
Monitoring Network Activity
Monitoring Network Activity with Network Monitor The tool which you can utilize to both monitor and log network activity as it occurs on the network is the Network Monitor. You can use the information obtained from Network Monitor to optimize network traffic as well. Network Monitor stems directly from the Windows NT Network Monitor. Network Monitor is included with Windows Server 2003. The key administration tasks which you can perform using Network Monitor are summarized below: You can capture frames directly from the network which you are monitoring. You can Read More
NetBIOS Names
A NetBIOS name is an identifier that NetBIOS services running on a computer use. It is a combination of a 15 character (byte) name and a 16th character denoting the service. These names identify resources on the NetBIOS network. NetBIOS cannot do name resolution on the Internet because NetBIOS names are single part names and do not have any hierarchical structure. The NetBIOS namespace is flat, which means that there are no suffixes added to the NetBIOS name and that two computers cannot have the same NetBIOS name. This means Read More
Understanding Wireless Connections
Wireless Network Concepts Wireless local area networks are defined by the IEEE 802.11 specification. The process of connecting to a wireless network is often transparent to the user, and using a wireless network is pretty much the same as using a wired Ethernet network for the user. A wireless network is classed, based on the scope of the network. This is also very much like classing wired networking. The different categories of wireless networks are: Wireless local area networks (WLANs): WLANs make it possible for data to be shared within Read More
Network Load Balancing
Network Load Balancing Overview Network Load Balancing (NLB), included in Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 can be used if you need to provide increased levels of availability for TCP/IP applications. All versions of Windows Server 2003 include NLB. While NLB is automatically installed, it is not enabled. In a NLB cluster, client requests are load balanced between the servers residing in the NLB cluster, as specified by configured load balancing parameters. Servers can be configured to share the processing of client requests. NLB can also reroute any requests that Read More


Share on: