Understanding the Limitations of IPv4 Before moving on the to an in-depth discussion of IPv6, lets first look at the limitations of IPv4: The IPv4 addresses are somewhat scarce, even though it allows for 4,294,967,296 possible addresses. Because of this limitation, organizations are forced to utilize Network Address Translator (NAT) to map a public IP address to several private IP addresses. NAT typically creates performance and application bottlenecks. The increase in devices that are connected to the Internet would lead to the depletion of IPv4 address space. There is a Read More
How to Verify if a Windows CD is Legal
Over the years, some the products which have seen a tremendous amount of counterfeiting are Microsoft Windows Products. While counterfeit MS software might be cheap for those that use it, it can also be less stable – allowing access by viruses, trojans, and malware. It also should be noted that in some situations – such as in using counterfeit software in a corporate environment, heavy fines can be risked. If you are purchasing a new or used computer with Windows software or buying Windows software via a retail outlet, here Read More
Using the Remote Control SMS Feature
SMS Remote Control Tools Overview SMS Remote tools enable administrators to control remote client computers. The Remote Tools set provides the following features: Remote control Remote reboot Remote chat Remote execute File transfer Windows diagnostics DOS diagnostics Ping test Remote Tools are categorized as follows: Remote Diagnostics: Provides the capabilities listed here: Control a client computer's mouse and keyboard Execute a program Copy files Reboot View the configuration settings of client computers. Remote Functions: Indicates whether the SMS administrator or the local user manages the level of access of the Read More
NetBIOS Node Types
A NetBIOS node type is a method that a computer uses to resolve a NetBIOS name into an IP address. A NetBIOS node type allows an administrator to configure the order and method that a client uses when resolving NetBIOS names to IP addresses. Understanding how the various node types function will help users to properly configure their WINS solution. Windows Server supports the following node types: B-node (broadcast): it uses broadcasts for name resolution and registration. In a large network, a broadcast increases the network’s load. In addition, routers Read More
Understanding NetBIOS Name Resolution
NetBIOS, broadcasts names to listening nodes on the network. NetBIOS utilizes a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) query to broadcast names. NetBIOS names identified computers on the network before the introduction of Windows 2000. The NetBIOS name is resolved to an IP address through Windows Internet Name Service (WINS), broadcasting, or the LMHOSTS file. If the LAN is a NetBIOS LAN, the NetBIOS name is then the network address. The NetBIOS name is assigned by an administrator when the operating system is installed. To enable communication, the following requirements exist: NetBIOS Read More
Managing the IIS Metabase
An Overview of the IIS Metabase With the introduction of IIS 4, came the introduction of the metabase. IIS configuration information was no longer stored in the Registry, but in the new metabase structure. Some IIS configuration settings however still remained stored in the Registry, under the following keys: HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftInetMgrParameters HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesInetInfoParameters HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesASPParameters HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesHttpParametersLogBufferSize HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW3SVCParameters HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesMSFTPSVCParameters In IIS 4, separating the majority of IIS configuration settings into the metabase; speeded up access to the information. The issue with the metabase in IIS 4 and IIS 5 was that it was a Read More
ReadyBoost
Ready Boost is an operating system feature introduced with Microsoft's Windows Vista operating system. The best way to improve the functioning of a PC is to increase its memory as increased memory enables more applications to operate on the computer. But this is not possible in many PCs as they have a maximum limit of memory and to increase it will call for upgrading memory which is very costly and some machines have limited expansion capabilities which don't enable the expansion. It is here that the Windows Vista comes to Read More
How to Change the Swap File Settings
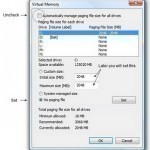
Prior to revising your Virtual Memory settings, you should check on how much Virtual Memory you would need, based on how much RAM you do have and how memory-intensive your normal applications are. Specifying Virtual Memory Settings The best way to do this is by installing the built-in System Monitor applet from the Add/Remove Program component in the Control Panel. Go to Windows Setup, highlight System Tools and click Details. Put a check on System Monitor and then hit the OK button, and exit the program. A prompt will appear Read More
Macintosh and Windows Server Integration
Macintosh Services Overview While in the earlier days, it was somewhat difficult to integrate Macintosh networks and Windows networks because each operating system basically used different protocols, and files structures and systems. To deal with these integration issues, Microsoft has since introduced the File Server for Macintosh (FSM) and Print Server for Macintosh (PSM) services with Windows NT Server. These FSM and PSM Macintosh services are also included with Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003. When the FSM and PSM Macintosh services are installed, it enables Macintosh clients to access Read More
dllhost.exe
Dllhost.exe is an essential Windows process that allows executable files to access DLL files that are stored on a computer. A DLL (Dynamic Link Library) file contains source code or parameters for running or communicating with a specific application or device. Because every executable file or program on a computer uses DLL files, Dllhost.exe is very important for the computer’s proper performance and removing or modifying it may cause the computer to crash or stop working properly. Dllhost.exe can be found in the Windows folder’s System32 subfolder on the computer’s primary Read More


Share on: