MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching)
MPLS stands for Multi Protocol Label Switching. The MPLS is often referred to as the layer in between the Data Link and Network layers because of where it operates. The MPLS serves as a method to forward packets of data easily by using labels.
What are the Data Link and Network layers?
In the seven-layer OSI model, a model used to explain how a computer operates and communicates within itself. The Data Link and Network Layers are parts of this model, and correspond to the second and third layers respectively. The former allows connections such as Ethernet and wireless Local Area Networks, while the latter is analogous to Internet Protocol.
Why does it matter that MPLS lies in-between these two layers?
The MPLS forwards data that pertains to both Layer 2 applications, such as Ethernet frames, and Layer 3 applications, such as IP packets. For this reason, it is often considered to be in between the two recognized layers.
On a more technical level, the label left by the MPLS is also left in between the second and third layers of a packet of data.
What is a label?
In short, a label is a method to identify a packet of data and forward it to a destination quickly. Labels indicate a FEC that each data packet must follow.
What is a FEC?
FEC stands for Forwarding Equivalency Class. The FEC refers to a group of data packets that all should arrive at the same destination and thus are all labeled the same. Thus the FEC can be used to direct packets and are included within labels.
What are the benefits of using MPLS?
Because the MPLS allows data packets to be labeled and sent better, there are smaller problems to the network with regards to excess traffic. This allows for a greater efficiency within a network and a wider range of flexibility as to managing networks.
What is an MPLS Network
An MPLS network is a private network technology that uses a Virtual Private Network (VPN) on top of shared network infrastructure similar to an ATM or FrameRelay network. This technology’s IP backbone uses Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS), which makes the network easier to customize and administer, and makes the network safer and more reliable. MPLS eliminates IP network deficiencies while ensuring high service quality for data, video, and voice applications on the network. MPLS networks can now provide high performance network services for companies at a low cost.
MPLS networks differ from traditional networks because they connect a large number of devices across long distances by tunneling through the Internet.
Applications
MPLS networks are generally used for communication and data trafficking purposes. Most large companies have representatives in many different locations. Each of these representatives must be able to communicate with the company’s headquarters and regional offices. MPLS networks allow them to do this by forwarding data packets to each representative on the way to the company’s headquarters.
How MPLS Networks Work
An MPLS network is a cloud-like system of computers and other devices that all communicate with each other by assigning labels to data packets so that they can be forwarded from one device to another. For example, if Device A wishes to send a data packet to Device E, Device A will insert a header in the data packet with a label stack that contains information about the data packet, where it came from, and where it is going. Device A will then send the data packet to Device B, Device B will send the data packet to Device C, Device C will send the data packet to Device D, and Device D will send the data packet to Device E. Each device strips away past labels and adds new ones in order to keep forwarding the data packet to where it needs to go.
Advantages of Virtual Private Networks
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) lets companies take advantage of public Internet infrastructure for significantly reduced costs. Instead of relying on public hot-spots, a VPN ensures that the network user has better security and an improved service quality compared to public connections. VPNs also provide better network data packet integrity, while reducing the latency and jitter issues found on public networks.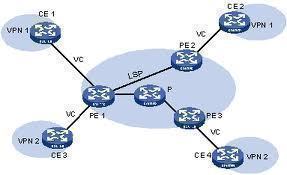
MPLS Network Advantages
MPLS networks allow employees, students, and organization members to be connected across far distances, while still enjoying the same service quality that is experienced in their home office. They connect all devices within the network to each other without using cables, access points, or other tethering equipment. MPLS networks are publicly available to anyone who has access to the Internet, but security protocols allow the network to handle all data packets privately and deny access to all other users.
Since an MPLS VPN incorporates multiple network protocols, users can use VoIP services, video, TDM telephone, and other network specific services while on the road or working in a different location. Advances in computer networking hardware and software have reduced MPLS network costs, making them more commonly implemented over a VPN. An MPLS is more efficient than a similarly constructed frame relay network since the frame relay technique uses small ATM network cells. Although still used in a limited fashion, many providers have switched from frame relay network architectures to MPLS. Point to point networking is also compared to MPLS. However, it has the disadvantage of not being scalable without increasing infrastructure and costs.
Future MPLS Developments
Over the past few years, it has become more popular for large networks to be referred to as “clouds.” MPLS is commonly referred to in the same manner since it uses label switching technology to tag input data/packets with the destination, provider, and any quality of service requirements to support information use. The network then uses tag switches or label routers to deliver the information to the appropriate destination at the right level of quality. As the number of MPLS networks continue to increase, the number and employment of cloud services on organizations’ networks will continue to increase.


Comments - 3 Responses to “MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching)”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.