A broadcast address is an IP address that targets all systems on a specific subnet instead of single hosts. The broadcast address of any IP address can be calculated by taking the bit compliment of the subnet mask, sometimes referred to as the reverse mask, and then applying it with a bitwise OR calculation to the IP address in question. Some systems that are derived from BSD use zeros-broadcasts instead of ones-broadcasts. This means that when a broadcast address is created, the host area of the IP address is filled Read More
Packet Sniffers
Packet sniffing is listening (with software) to the raw network device for interesting packets. When the software sees a packet that fits certain criteria, it logs it to a file. The most common criterion for an interesting packet is one that contains words like “login” or “password.” To packet sniff, obtain or code a packet sniffer that is capable of working with the type of network interface that the operating system supports: Network interfaces include: LLI NIT (Network Interface Tap) Ultrix Packet Filter DLPI (Data Link Provider Interface) BPF (Berkeley Read More
802.11n
Information technology group Wi-Fi Alliance or WFA has been testing a next generation, yet still pre-standard wireless networking program that would define wireless Internet of the future. Much ado has been tackled about the technology called 802.11n. For the average Internet user, who knows not too much about the standards and technicalities of the information technology tools, 802.11n is just another consumer electronics code. For the benefit of all computer users, it would be imperative if basic description and comprehensive yet simplified explanation about the code would be offered to Read More
How to Use PuTTY
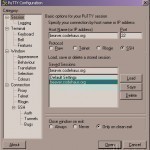
PuTTY is an open source terminal emulation program that accesses Telnet, SSH, and other TCP protocols and acts as a serial client for computers. The letters “TTY” in the name PuTTY represent the terminal application in the Unix and Linux Operating Systems (OSs) and is also short for teletype. The PuTTY application was first written to be used on computers running the Windows Operating System (OS) and can access centrally based web servers that are running the Linux or Unix OS. PuTTY Features Features included in the current PuTTY application Read More
Dark Fiber
In fiber optics, a dark fiber is any optical fibre that is currently not being used in the ever expanding fiber optics network. Because the fibers have already been laid out, they can be used by anyone should they be leased from the network service provider such as AT&T or Sprint. However, because they are not currently being used, they have gained the name dark fiber or unlit fiber. Why Is There Dark Fiber? The reason for dark fiber is a two fold answer. The first and foremost is the Read More
Ethernet Hub
For any two devices to be connected, they need a common place, or a hub, as it is called in the computer world. It basically connects multiple computers together. Most of the hubs available in the market today support Ethernet standards. This is why they are called Ethernet hubs, and are most commonly used in computers for networking purposes at home. Ethernet hubs are available in different types, depending on the speed of the network connection or broadband speed. Also, the number of ports supported by the hub varies, there Read More
Optical Networking
Modern technology has provided us with many things over the past few years, one of which is optical networking. By using optical networking, individuals and organizations alike are able to stay connected to the world much more efficiently and with faster data transfer rates than ever before. Fiber optics have revolutionized the world of communication, business, and entertainment in ways that we could not have possibly conceived of a decade ago. In this article, we will discuss optical networking, how it works, and various types of optical networks. What is Read More
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
SAML is the Security Assertion Markup Language. SAML is a derivative of XML which is designed for the exchange of authentication and authorization data. The purpose of SAML is to enable Single Sign-On for web applications. SAML utilizes TLS to ensure the confidentiality of authentication and authorization data during transit. SAML Standards SAML is defined by the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS). saml-conformance-2.0-os Conformance Requirements saml-core-2.0-os Assertions and Protocols saml-bindings-2.0-os Bindings saml-profiles-2.0-os Profiles saml-metadata-2.0-os Metadata saml-authn-context-2.0-os Authentication Context saml-sec-consider-2.0-os Security and Privacy Considerations saml-glossary-2.0-os SAML Glossary Read More
ISDN 30
ISDN 30 is a type of Integrated Service Digital Network system that is used for the transmission of voice and data over wires. ISDN 30 is one of the most economical and efficient communication systems. It is used in medium as well as large businesses. Through ISDN 30, business organizations and call centers can get high speed Internet connections at very economical rates. ISDN 30 connections can be obtained from the local telephone exchange. The speed that it provides may vary; the maximum is two Mbps. ISDN 30 consists of Read More
Fiber Optic Internet

Everyday, data transfer rates are getting faster and faster as technology gets better and demands get higher. To keep up with these faster data transfer needs, fiber optic Internet access has been introduced to the public. Fiber optic Internet uses pulses of light to create an electromagnetic carrier wave that can be used to send data at very high speeds. In this article, we will explain how fiber optic Internet works, compare fiber optics with coaxial Ethernet cables, compare fiber optics with wireless internet, explain what direct fiber and Read More


Share on: