Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a system that provides a constant supply of DC power to a computer network using the same Ethernet cables used for connectivity. Devices such as network cameras and IP telephones can hence be powered without the need for extra wiring. PoE is easy to maintain and requires little or no human intervention. Another name for PoE is Power over LAN (PoL). In order for Power over Ethernet to work effectively, the electrical current must flow through the data cable at the main supply entrance and Read More
Internet Backbone
In 2005, the one billionth Internet user logged on to the World Wide Web. Hundreds of thousands of new users log in for the first time each week. It is estimated that the 2 billion user mark will be reached in less than 10 years from now. There is no question that the World Wide Web is growing and becoming more important each day. More than ever, individuals and companies rely on the stability of the Internet for a constant exchange and display of important information. Virtually every financial institution Read More
RSN (Robust Secure Network)
RSN (Robust Secure Network) is a protocol for establishing secure communications over an 802.11 wireless network. RSN (Robust Secure Network) is part of the 802.11i standard. The RSN Protocol Process The RSN protocol functions as follows: The wireless NIC sends a Probe Request. The wireless access point sends a Probe Response with an RSN Information Exchange (IE) frame. The wireless NIC requests authentication via one of the approved methods. The wireless access point provides authentication for the wireless NIC. The wireless NIC sends an Association Request with an RSN Information Read More
HSCSD (High Speed Circuit Switched Data)
Fixed/Mobile Mobile Circuit/Packet Circuit Max Bandwidth 57.6Kb Range Coverage area of host network Frequency Frequency of host network Host Network GSM Definer ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) URL http://www.etsi.org/ HSCSD (High Speed Circuit Switched Data) is a specification for data transfer over GSM networks. HSCSD utilizes up to four 9.6Kb or 14.4Kb time slots, for a total bandwidth of 38.4Kb or 57.6Kb. 14.4Kb time slots are only available on GSM networks that operate at 1,800MHz. 900Mhz GSM networks are limited to 9.6Kb time slots. Therefore, HSCSD is limited to 38.4Kbps Read More
Attenuation
Attenuation is a reduction in signal strength over distance. Attenuation is a common problem of telecommunication cables that causes a decrease in data speeds on longer cables. Attenuation is also known as “loss” and can be countered by data repeaters and amplifiers. While attenuation is a problem for long cables, short cables do not usually experience high amounts of attenuation, even if the same amount of data is transferred. How Attenuation Works Attenuation is caused by resistance of electricity in the cable it is transferred through, which causes waste and Read More
How Unix and Windows traceroutes differ
The Unix/Linux `traceroute` command and the Microsoft Windows `tracert` commands both accomplish the task of tracing network paths, but they do it in slightly different ways. Both of these tools for tracing network routes send out a packet wth TTL (Time To Live) set to 1 and report it's destnation. Then, they send out a packet with TTL=2 and report it's destination. They continue until the packets reach their final destination or the TTL limit is exceeded. The difference is that Unix/Linux `traceroute` uses UDP (User Datagram Protocol) packets to Read More
What is PCAP?
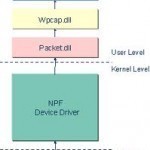
PCAP (Packet Capture) is a protocol for wireless Internet communication that allows a computer or device to receive incoming radio signals from another device and convert those signals into usable information. It allows a wireless device to convert information into radio signals in order to transfer them to another device. PCAP runs in the background of all wireless devices and plays a critical role in wireless communication, though it is seldom recognized. It has many uses and millions of computer users around the world use it daily. How PCAP Works Read More
What is a TFTP Server?
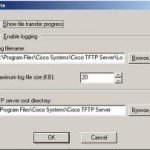
A Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server is based on a simple Fire Transfer Protocol (FTP) that was first defined in 1980. TFTP books routers and other computers that do not have storage devices. It also transfers small files between two or more computer network hosts such as a transfer initiated on a remote X Window System terminal. TFTP servers are also based on the traditional EFTP protocol that was part of the PUP protocol tool suite and is normally one of the first protocols used on a new host Read More
Application Layer
The application layer of a software is a protocol that is used for communication between a software and the network layers that it uses. The application layer allows a computer’s network to interpret requests made by the program and allows the program to interpret data from the network. Likewise, the application layer ensures that both parties are available and can communicate with another, authenticates messages from both parties, and ensures that both parties agree about privacy, data integrity, and error recovery. How An Application Layer Works The application layer Read More
Wireless Mesh Network
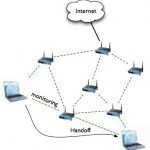
A wireless mesh network relies on radio signals to allow several devices within a coverage area to communicate with each other. Wireless mesh networks are often used in conjunction with other networks in order to give users reliability and stability. This is because wireless mesh networks communicate with each other through any device within the coverage area and automatically restore communication if one device stops working. Wireless mesh networks include everything that other networks do (router/gateway, clients, etc.) but do not necessarily need to connect to the Internet. How Wireless Read More


Share on: