An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique address that different computers on a computer network use to identify and communicate with one another. An IP address is used as an identifier to find electronic devices connected to one another on a network. Therefore, each device in the network must have its own unique address. An IP address is like a mailing address that is used to deliver data (files) to a computer. Some IP addresses are meant to be unique within the scope of the Internet, whereas others are Read More
Parallel Printer Cable
This cable can be used to connect a parallel printer to the parallel port on a PC. The phrase parallel cable can be ambigous as it shelters numerous different specifications, not all of which are simple PC to printer type. The parallel port socket on a computer uses 25 pins. There are two types of parallel printer cable that are widely used for PCs. The old "standard" IBM Printer cable and the newer IEEE 1284 bi-directional cable commonly sold today. 25 pin male connector 36 pin Centronics male connector Parallel Read More
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol)

The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) is a simpler version of the Network Time Protocol (NTP). SNTP synchronizes the time between networked computer systems and is relied on when data is being transferred via the Internet. The NTP protocol is one of the most established protocols still used on the Internet. It uses a GPS or radio clock to tell time and is accurate past the seconds place. Why is the SNTP Necessary? The need for precise time synchronization has continued to increase with the evolution of computer technology over Read More
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) is part of a draft standard from the IEEE 802.11i working group. TKIP utilizes the RC4 stream cipher with 128-bit keys for encryption and 64-bit keys for authentication. TKIP is an enhancement to WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) security. TKIP enhances WEP by adding a per-packet key mixing function to de-correlate the public initialization vectors (IVs) from weak keys. TKIP also enhances WEP by adding a rekeying mechanism to provide fresh encryption and integrity keys. This makes TKIP protected networks more resistant to cryptanalytic attacks involving Read More
192.168.2.1 – What Are its Uses and Why is it Important?
192.168.2.1 is a private IP address commonly used by the SMC and Belkin router manufacturers for device setup and troubleshooting. SMC and Belkin specialize in manufacturing home networking equipment that competes with Netgear, D-Link, and Linksys brands in the marketplace. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) does not grant exclusive use of the IP address to these companies; however, as other network equipment manufacturers are free to use the IP address if required or desired. If another router or networking device is installed on a local network which uses 192.168.2.1, Read More
Ethernet Crossover Cable
An Ethernet crossover cable can be used to directly connect two network devices through Ethernet. These can either be single computers or they can be networks. Ethernet crossover cables are commonly used for temporarily networking two devices in the absence of a network router, switch, or hub. The principle is the same, but the connection speeds and methods are different. The crossover cable’s function is to send and receive data. Ethernet crossover cables enable complex data transfers between computers, routers, and networks. Unlike standard Ethernet cables, the internal wiring of Read More
Public DNS Servers

DNS (Domain Name System) servers are designed to allow networked devices such as computers, phones, and other servers to look up address records in DNS tables. The majority of DNS servers are configured to provide service to the organizations or people that own or pay service fees for the hardware. There are a number of public DNS servers that will provide DNS resolutions for requesting computers or people. The majority of these servers are purposely public; however, some become public due to misconfiguration or malicious behavior. These typically get fixed Read More
Understanding Frame Relay
Frame Relay is a protocol for transmitting data over a wide area network (WAN). It was designed to use across ISDN interfaces but it is now used over an assortment of other network interfaces. Once one becomes a master of frame relay design and configuration, it is much easier to obtain a strong understanding of x.25, ATM, and SMDS. Frame relay operates at the physical and data link layers of the OSI model. Frame relay is an example of packet switched technology. In a packet switched network, end stations share Read More
ISDN BRI
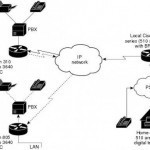
ISDN BRI (Basic Rate Interface) is a standard Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) service meant for residential and small scale business Internet connections. There is another type of ISDN configuration called the Primary Rate Interface (PRI) that is designed to provide higher bandwidth. The BRI configuration defined in the physical layer standard I.430 produced by the ITU. Both the BRI and PRI are designed similarly. That is, both make use of the B and D channels for data communication, but in different combinations. B Channel or the Bearer Channel is Read More
IP Address Spoofing
IP address spoofing denotes the action of generating IP packets with fake source IP addresses in order to impersonate other systems or to protect the identity of the sender. Spoofing can also refer to forging or using fake headers on emails or netnews to – again – protect the identity of the sender and to mislead the receiver or the network as to the origin and validity of sent data. Basics of IP Address Spoofing The Internet Protocol or IP is the fundamental protocol for sending/receiving data over computer networks Read More


Share on: