RS-232 stands for Recommended Standard 232. It is a standard for serial binary data signals connecting between a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and a Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE). It is widely implemented in computer serial ports communication – roadmap for the way devices speak to each other using serial ports. RS-232 is radically identical to ITU V.24 (signal description and names) and V.28 (electrical). RS232 is an Active LOW voltage driven interface and operates at +12V to -12V. RS232 DB25 Pinouts Pin 1 Protective Ground Pin 2 Transmit Data Pin Read More
Fiber Optics
Fiber optic technology makes use of light to carry digital signals via optical cables. Fiber optic cables are very thin glass wires made from extremely pure optical glass. This technology is based on the concept of light reflection. In the case of fiber optics technology, light carrying digital signals is reflected inside the optical cable to transfer information. Total internal reflection is the principle behind the success of this technology. Fiber Optics: Glass Anatomy A fiber optic cable is basically made-up of three parts: the core, the cladding and the Read More
WiFi Repeater
What is a WiFi Repeater? A WiFi repeater is a device that is able to pick up a WiFi signal, amplify it, and redirect it to another device. WiFi repeaters are often used for commercial purposes because a wireless router can only broadcast a signal up to a certain distance and wireless adapters can only receive the router's signal if the router is within a certain range. A device's range is sometimes not large enough to cover an entire infrastructure. Fortunately, WiFi repeaters can be used to effectively double the Read More
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, also called coax, is used to transmit radio frequency (RF) signals. It has low emission losses and provides protection from electromagnetic interference, allowing signals with low power to be transmitted over longer distances. Coaxial cable is comprised of an inner core, insulator, shield, and outer cover. It is called coaxial because these sections all share the same axis. There are many different types of coaxial cable, each one with different physical and electronic properties designed for specific tasks. It is commonly used for carrying cable television signals along Read More
Cat 6
Cat 6 (Category 6) is a cable standard used mainly for Ethernet computer networking, security systems, and telephone services. Cat 6 cable is backward compatible with the Cat 5, Cat 5E, and Cat 3 cable standards. Category 6 cable is capable of transmitting voice and data up to 155 Mbps (mega bits per second), with possible transmission frequencies up to 550 MHz. Cat 6 carries Ethernet 10Base-T, 100Base-TX, and 1000Base-T (Gigabit Ethernet) connections. Cat 6 cable is backed with more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise than earlier cabling Read More
What is an OTDR?

An OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) measures the time and intensity of light reflected on optical fiber in a fiber optic cable. It is primarily used to troubleshoot fiber lines to identify splices, bends, and faults, and is specifically geared to locating any light loss in a fiber line. Why is Identifying Light Loss Important? When a fiber optic cable experiences light loss, it interferes with data transmission. OTDRs can detect light loss and identify the trouble areas in the line, which helps technicians to make repairs. Companies that own Read More
Null Modem Cable
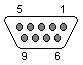
A null modem cable will enable you to connect two computers together for serial communications. It is a particularly designed cable that permits anyone to connect two computers directly to each other via their communications ports called RS-232 ports. Serial communications with RS232 is one of the oldest and most widely spread communication methods in computer realm. Null modems are specially helpful with portable computers because they enable the portable computer to exchange data with a bigger machine. Null modem cables have the TD (Transmit Data) and RD (Recieve Data) Read More
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
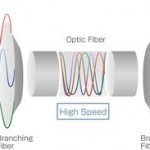
DWDM stands for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing. DWDM is a technology used to increase the capacity of fiber optics that results in faster transfers of data. What are fiber optics? Fiber optics are very thin and small fibers that are used to transmit data and light throughout a computer and network. How does DWDM affect fibers? The DWDM takes different signals and sends them at varying wavelengths simultaneously along a single fiber. This allows a fiber to increase its capacity and in effect makes it seem as if there are Read More
How to Use Cable Splicing Tools
Cable splicing tools are a fast and effective way to connect two wires or cables into one. Most cable splicing tools look like pliers; however others are more like scissors or utility knives. Here are some tips on how to best use these cable splicing tools: For Larger, Thicker Cables First, the type of splicing tool you will need depends upon the type of cable you would like to splice. Very tough cable sheaths usually require a plier-like splicing tool to cut deep into the sheath. Remember that your goal Read More
Ethernet Card
The system that helps connect a computer to an Ethernet network is called an Ethernet card. Another name for such a card is Network Interface Card (NIC). It can be inserted into one of the slots provided on the motherboard of the computer. Each of these cards has a unique identification number, known as the MAC address. Ever since their inception by the Xerox Company, Ethernet cards have managed to find their way into nearly every single computer in the world. The Ethernet Card – An Easier Alternative for Data Read More


Share on: