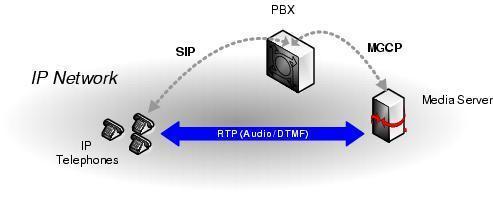
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is used to encapsulate VoIP data packets inside UDP packets.
RTP is defined in RFC 3550 – RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications.
RTP provides end-to-end network transport functions suitable for applications transmitting real-time data, such as audio, video or simulation data, over multicast or unicast network services. RTP does not address resource reservation and does not guarantee quality-of-service for real-time services. The data transport is augmented by a control protocol (RTCP) to allow monitoring of the data delivery in a manner scalable to large multicast networks, and to provide minimal control and identification functionality. RTP and RTCP are designed to be independent of the underlying transport and network layers. The protocol supports the use of RTP-level translators and mixers.
Other RFCs which document RTP include:
- RFC 3551 – RTP Profile for Audio and Video Conferences with Minimal Control
- RFC 2032 – RTP Payload Format for H.261 Video Streams
- RFC 3158 – RTP Testing Strategies
- RFC 3605 – Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP) attribute in Session Description Protocol (SDP)
- RFC 3611 – RTP Control Protocol Extended Reports (RTCP XR)
- RFC 3711 – The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)


Comments - One Response to “RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.