Stars form within clouds of dust that are scattered around the galaxies of our Universe. In essence, a star is dust that is pulled toward a central point of gravity and, when this happens, begins to heat up. The formation of a star results in something like our own Sun which took 50 million years to turn into what it is today. And, our Sun will last another five billion years–or ten billion years in total from the formation of the Universe. Within these clouds of dust there is a Read More
What Are Asteroids Made Of?
An asteroid is a large chunk of matter made up of rock and/or metal that is either found within the Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter or orbiting the solar system. They can range in size from the size of a particle of dust to many miles across; therefore, there are many different ways to classify an asteroid. However, when it comes to what their made of, there are only three ways to classify them and group them together. The first way which is the first material that they're made Read More
Blackbody Radiation
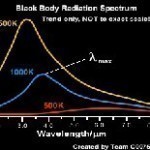
Blackbody radiation refers to the electromagnetic radiation that a blackbody material expels. Blackbody materials are substances that absorb all electromagnetic radiation that comes in contact with it, including light and heat. While a perfect blackbody material does not exist in nature, substances such as ash, soot, and granite come close. When a blackbody material is irradiated with light or radio frequencies, it circulates the energy and releases it as heat. Alternatively, when the blackbody material is irradiated with heat, it dispenses the energy as a radio frequency. In this way, Read More
What is a Geosynchronous Orbit?

A geosynchronous orbit is when a satellite or other device’s orbit matches the Earth’s rotation so that the satellite travels around the Earth in a straight line and stays at the same point in the sky relative to the Earth. This means that as the Earth rotates, the satellites rotates around the Earth at the same speed so that its relative position never changes. Geosynchronous orbits are used for a number of purposes, including monitoring a specific region and communicating with Earth-based systems. Geosynchronous orbits include geostationary orbits, super-synchronous orbits, sub-synchronous orbits, and graveyard Read More
What Causes the Phases of the Moon?
The phases of the moon are caused by the location of the moon in relation to the Earth. In other words, as the moon rotates around the Earth, sun hits it in different angles and therefore, this causes the moon to undergo different phases. Based on the time of the month, the side of the moon that we see will experience more sunlight on it and then less sunlight. The Phases of the Moon When the moon "starts" its cycle of phases, it is known as a New Moon. This Read More
Law of Universal Gravitation

The law of universal gravitation gives the attraction force between two objects due to gravity. Definition: For any pair of objects, they attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers of mass. Gravitational constant (G): the proportionality constant is known as gravitational constant, it is a positive number and its value is about 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2. Center of Mass: For a homogenous sphere the Read More
Ion Propulsion

Ion propulsion refers to a method of space travel in which accelerating ions, rather than traditional chemical rockets, speed up a spacecraft. While ion propulsion produces very little thrust in comparison to chemical propulsion, it produces consistent acceleration that allows the spacecraft to eventually travel faster than a chemical rocket would. Ion propulsion requires an environment with no radical ions, which means that it cannot be used for air travel, and only works well in interplanetary travel due to its exponential acceleration. Ion propulsion also requires a rather large amount Read More
Space Elevator
A space elevator will facilitate faster and cheaper travel of humans, materials and equipment from Earth to space. This structure is slated to replace conventional 'spaceships'. Scientists and engineers are divided when it comes to the space elevator design. There are those who are convinced that tethering is necessary and there are those who believe otherwise. Tethered designs are more widely accepted than non-tethered designs. Components of a Tethered Space Elevator Tethered space elevators require a base station. The base station can be found on a huge floating barge out Read More
Perigee

Perigee is a term used to describe the closest point at which an object orbits the Earth or another object in space. When an object is at its perigee, it travels faster than it does at any other point in its orbit because it is under the influence of the strongest gravitational force that its source gives, which propels it further in its orbital path. How Perigee Works Although there are several different types of orbits that an object can take around its source, most objects travel in an elliptical Read More
Robonaut
A robonaut is a robot designed to assist humans in space exploration missions. As temperatures in space can range from -100 degrees Celsius to 120 degrees Celsius, astronauts need to wear space suits that cost 12 million dollars apiece. They also need at least a few hours of preparation before they can respond to any emergencies like external repairs on an international space station caused by collisions with space matter. Because of these inherent difficulties that human astronauts face, robonauts that can be fielded in far less time and with Read More


Share on: