A laser printer unlike an inkjet printer uses a laser light beam for printing operations. It is also distinct from other printers because of its exceptional printing speed as well as highly accurate rendering. It utilizes a xerographic (a process of creating an image by the action of light on a specifically coated charged plate) printing. Some laser printers in the market can print a hundred colored pages and two hundred non-colored pages every minute. Resolution is a key characteristic of laser printer, measured in dots per inch (dpi). The Read More
Oersted

The Oersted (Oe) is the unit of measurement for a magnetizing field that is also known as an H-field, intensity, or a magnetic field. The Oersted was named after a Danish physicist and philosopher, Hans Oersted, who discovered the connection between electricity and magnetism in 1819. Who was Hans Oersted? Hans Oersted was a Danish philosopher and physicist who is most famous for discovering electromagnetism. This discovery led to research circles placing a significant amount of focus on notable scientists, Ampère and Arago’s electrodynamic research. The scientific community then discovered that electrically Read More
Metamaterials

A metamaterial is artificially designed and its properties are not found in nature. It generally gains its properties through construction rather than its composition. In fact, metamaterials are usually made from extremely interconnected bonds at the nano level. This allows them to be used in applications that involve manipulating light, sound, vibrations, microwave radiation, or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. Metamaterials also allow an object to be lighter, more durable/flexible, or be more electrically conductive. How Metamaterials Work A metamaterial is generally fabricated at the nano level in a laboratory Read More
What is a Barrier Isolator?

A barrier isolator is a device that is the physical barrier between a laboratory technician or observers and laboratory work that is in progress. The pharmaceutical industry is the largest barrier isolator user. Modern barrier isolators can be operated at ambient, positive, or negative environmental pressures. They also protect people, the environment, a product, or a combination of these. Many industries use barrier isolators, resulting in higher quality products that require a clean production environment and reduced industrial risk for company employees. History of the Barrier Isolator As the pharmaceutical Read More
What is Stereolithography?
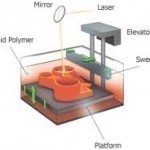
Stereolithography is a recently discovered process by which products, especially prototypes, can be constructed one layer at a time by using UV-curable photopolymer resins and a UV laser. While stereolithography cannot create every type of material, it produces a wide variety of products for testing, analysis, or review. Stereolithography can be used for a wide variety of applications and is most widely used to produce prototypes for the 3D printing industry. How Stereolithography Works Stereolithography is a complex process that requires a vat of liquefied, UV-curable photopolymer resins. A UV Read More
Cadmium Telluride
Cadmium Telluride is one of the most toxic and deadly substances known to man. It is a by-product of lead, zinc, and copper mining and is also naturally found in soil and water. Despite its toxicity, cadmium telluride is still frequently used because it has highly sought after physical and chemical properties. What Are the Properties of Cadmium Telluride? Cadmium telluride has a high resistance to chemicals and corrosion as well as a high tolerance for extreme temperatures. The substance also has a low melting point and is considered an Read More
Electric Field Strength
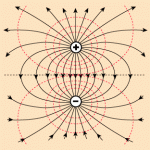
Electric field strength refers to the intensity of an electric field and is a measurement of the amount of energy present in an electric field. Electric field strength plays a major role in power grids, electronic equipment, electromagnetic devices, and a variety of other electrical systems. This is because devices must be able to calculate how much electricity is coming into the system, how much electricity is being directed towards a specific function, and how much electricity each function requires in order to safely power a wide variety of appliances. Read More
Electric Cars

Electric cars (or Battery Electric Cars) utilize electrical energy for motion instead of relying on energy generated by burning fuel. Batteries are the main source of energy, and are used to power electric motors in order to produce wheel or axle movement History of Electric Cars In the mid-19th century Robert Anderson, a Scottish businessman, came up with the early version of an electric vehicle that more or less resembles the carriage that was popular in his time. This car came before the invention and perfection of cars that run Read More
What Fuels Are Used in Power Plants?
There are many different types of power plants. Depending on the type of fuel someone wants to use determines what kind of power plant someone would build. The most powerful power plant is a nuclear power plant, but this is also the most controversial because of events such as Chernobyl and because it is difficult to get rid of the nuclear waste. However, the ultimate purpose of most power plants is to spin the turbine which, in turn, creates electricity. Gas Power Plant With a gas power plant, they take Read More
Invisibility Cloak
The search for invisibility technology has been the focus of much scientific research. Studies delving into its mechanics and possibilities have been in motion as early as the 1960s. Ivan Sutherland (Harvard University Professor) made groundbreaking research on the subject of scientific basis of visual invisibility through the technology dubbed as augmented reality. Augmented Reality and the Science of Invisibility The concept of augmented reality is the infusion of additional visual stimuli into an experience of time and space. With the aid of visual effects, a person experiencing augmented reality Read More


Share on: