An atomic force microscope, or AFM, is an instrument for mapping and measuring surface features of extremely small objects – from a carbon atom that is 0.25 nanometers (nm) or 2.5 Angstroms in diameter to a cross section of human hair (approximately 80 microns in diameter). Basic Principles of an Atomic Force Microscope The atomic force microscope is basically a miniaturized cantilever (a tiny beam is anchored at one end while another projects out into space like a diving board) with a tiny, pointed probe (with an extremely fine ceramic Read More
Robonaut
A robonaut is a robot designed to assist humans in space exploration missions. As temperatures in space can range from -100 degrees Celsius to 120 degrees Celsius, astronauts need to wear space suits that cost 12 million dollars apiece. They also need at least a few hours of preparation before they can respond to any emergencies like external repairs on an international space station caused by collisions with space matter. Because of these inherent difficulties that human astronauts face, robonauts that can be fielded in far less time and with Read More
What is Photolithography?
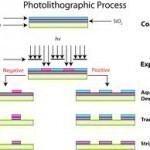
Photolithography is the process of making integrated circuits through optical erosion. Rather than directly cutting into an integrated circuit, photolithography is used due to its ability to perform more precise incisions. Photolithography is a highly complex technique and requires both an extremely clean substrate surface and ideal temperature conditions. It can only be used to produce flat surfaces. Despite this, photolithography is the most popular technique used to make integrated circuits. How Photolithography Works Photolithography begins with a substrate that has been previously cleaned with water or a chemical and Read More
Why is Geography Important?
While many of us labored to learn geography in school, we always wondered why it mattered. Here are some reasons why a sound understanding of geography is more important today than ever before. Politics We live in a world that is shaped by the political climate in various locations around the globe. In order to understand the mindset of modern day politicians, we can often get valuable clues by looking at the present geography of the country, state, or province they serve. At some point in time, that geography was Read More
Cold Fusion
Cold fusion refers to fusion reactions that occur at room temperature under normal pressure, using ordinary, simple devices. Fusion Fusion happens when two atomic nuclei come together to form a new, heavier nuclei. This is not easily accomplished because of a basic scientific principle: oppositely charged particles attract while similarly-charged particles repel each other. Since atomic nuclei (as in hydrogen protons) are similar-charged particles, their natural tendency is to repel each other and thus prevent fusion reaction. Scientists have discovered, however, that this natural repelling action turns into a powerful Read More
How Does a Coal Power Plant Work?
One of the oldest ways in which humans have created electricity is via coal energy conversion. The fundamental reason for this is that coal is an easy resource to find and the process for converting coal to electricity is a straight forward one. However, environmentalists have discouraged coal energy conversion in recent years because of its contribution to green house gases and the possibility that it could contribute to global warming. However, a coal power plant can create considerable energy, which is why there are still advocates for coal power Read More
What is Microfarad?

The term microfarad is used to describe a unit of capacitance that is 0.000001 farad. The symbol that represents a microfarad is µF. It is commonly used in utility alternating-current and audio frequency circuits. The capacitors that are found in them normally have a rating of 1 µF or more. However, even smaller capacitors are used in radio frequency systems. In this case, the picofarad (pF) is used instead of the microfarad. Audio frequency circuits use capacitors that are rated from 0.01 µF to 100 µF, and the capacitance in Read More
Magnetic Air Car
A magnetic air car is a concept car that Magnetic Air Cars, Inc. designed and developed. The company is based in San Jose and currently holds the patent to the technology, albeit that it is understood that J.M. Custer from Piggott, Arkansas originally created the magnetic air car in 1932. The car ran on compressed air that an oscillating magnet generated. Although the car worked and did not run on fuel, the idea did not become popular due to cheap gasoline and the emergence of the much faster automobile. While Read More
How Does the Biuret Test Work?
The biuret test is one in which a researcher can determine whether a mixture has peptide bonds in it or not. By using the biuret test, in seconds an individual knows if they are there. Once they know that the peptide bonds are, in fact, there, they can then attempt to measure the amount of peptide bonds in it by using the Beer-Lambert Law. How Does it Work? A small amount of the mixture that is believed to have peptide bonds in it is added to a test tube and Read More
How a Volcano Erupts

A volcano is any opening in the Earth’s surface that allows molten rock and volcanic gases to escape from far below the Earth’s surface. Although many volcanoes are mountainous in shape, a volcano can exist in nearly any form, including volcanic vents on the ocean floor, ice volcanoes, which have been found on a variety of other planets, and volcanoes that are simply a crater in the ground. Despite the variances in the shape of volcanoes, they all erupt in relatively the same way. The process begins when the pressure Read More


Share on: