Cryogenics is the branch of physics that deals with the production of extremely low temperatures – usually lower than -238 degrees Fahrenheit – and it specifically looks into how materials behave when they are exposed to such temperatures. The experiments performed by Sir Humphry Davy and Michael Faraday paved the way for this new field of physics. Popular literature, however, often mixes up cryogenics with cryonics or the use of cryogenics to preserve biological matter. Cryogenics, literally "cold production," is also a commonly used term when referring to a state Read More
Ozone Generators

Ozone or O3, is a molecule similar to oxygen that is made up of three oxygen atoms. While ozone in the lower atmosphere is harmful to humans, plants, and animals, causing respiratory problems in humans and animals while burning some types of plants, ozone in the upper atmosphere, known as the “ozone layer”, is highly effective at preventing harmful electromagnetic radiation from the Sun and other stars from reaching the Earth. By doing this, ozone is responsible for limiting the effects of global warming. While ozone in the lower atmosphere Read More
What is a Plastic Injection Molding Machine?

A plastic injection molding machine or injection press is a device that melts plastics and materials made from other polymers, and injects them into a mold. Plastic injection molding machines are most often used to recycle plastic, but are also the primary device responsible for producing plastic objects in the first place. They use a technique known as injection molding and mold a wide variety of materials, despite the name. How a Plastic Injection Molding Machine Works Plastic injection molding machines’ plastic production processes may vary, but they all include Read More
Water-Based Bomb Inhibitors

Water-based bomb inhibitors are water-filled devices that are used to attenuate or weaken the effects of a bomb blast. Water is used as a bomb inhibitor for these devices as water has a relatively high mass and is relatively available in almost any area. Water-based bomb inhibitors are successful in reducing blast and fragmentation by 90%. They also eliminate the risk of fire, reduce loss of property as well as casualty incidence. Furthermore, it preserves forensic evidence. It’s easy to install, too. Bomb inhibitors are gaining popularity all over the Read More
How Traffic Lights Work

Many street lights are equipped with Traffic Signal Preemption systems like the 3M Opticom or the Tomar Strobecom. These systems enable emergency vehicles to change the traffic signals from Red to Green, and to change the traffic signals for others from Green to Red. This enables emergency vehicles to travel more quickly and more safely. These systems operate by means of a receiver mounted on the traffic signal and a transmitted mounted inside the emergency vehicle. The transmitter is an infrared light which is flashed at the receiver. The transmitter Read More
Blackbody Radiation
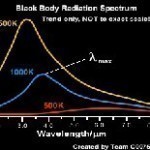
Blackbody radiation refers to the electromagnetic radiation that a blackbody material expels. Blackbody materials are substances that absorb all electromagnetic radiation that comes in contact with it, including light and heat. While a perfect blackbody material does not exist in nature, substances such as ash, soot, and granite come close. When a blackbody material is irradiated with light or radio frequencies, it circulates the energy and releases it as heat. Alternatively, when the blackbody material is irradiated with heat, it dispenses the energy as a radio frequency. In this way, Read More
How Do Rockets Work?
During World War II, there was a significant amount of research put into developing rocket-powered aircraft and missiles on both sides. The principles of rocket propulsion developed in this time period have served as the basis for the advancements seen in the field. These principles have taken man to the moon and are used on modern day military aircraft. Rocket propulsion systems, much like other types, rely on Newton’s third law of motion in order to generate thrust to create lift for both aircraft, rocket boosters, and missiles. Rocket Propulsion Read More
Methyl Iodide
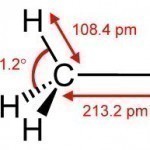
Methyl Iodide is a chemical compound that is relatively volatile. It is commonly found in the form of a dense, colorless liquid. It is also known as iodomethane and has the chemical formula CH3I (one carbon atom with three hydrogen atoms and a single iodine atom connected to it). Methyl iodide is a naturally occurring chemical compound that rice plantations emit in small amounts. Methyl Iodide Properties Methyl Iodide is a colorless liquid that turns purple when exposed to light for a long period of time because it is an Read More
How OnStar Works

OnStar was developed and deployed by General Motors for the purpose of providing fast and effective response in the event of vehicular accidents. OnStar has now been improved to provide more than the basic services. Now, it provides assistance with directions, car breakdown help as well as communications and leisure services. OnStar is a system for your automobile that performs many different functions, the most advertised being the fact that the company is alerted when you get in a car accident and they respond immediately by contacting you through the Read More
Auger Electron Spectroscopy
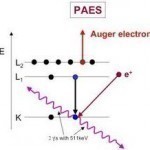
Pierre Auger discovered the Auger effect with x-rays that were involved in simultaneous cloud chamber usage. Auger observed that excited atoms emitted energetic electrons when the atoms relaxed. When the Auger effect was first discovered, it served little to the scientific community and was not utilized until the 1950s. The effect was then used to help improve the experimentation of chemical/compositional surface environments, in metallurgy, and in microelectronics. How Auger Electron Spectroscopy Works Auger Electron Spectroscopy is when specialized equipment that can test samples of materials is used to measure Read More


Share on: