The four dimensions are concepts in mathematics to describe different shapes. It is easy to understand a first dimension, second dimension and third dimension shape. All things are 3D in the world, but images can be 2D. A first dimension is as easy as a line. However, what is the fourth dimension? The fourth dimension is an abstract concept that takes two third dimension shapes and connects them together. What is the First Dimension? The first dimension is an interval. It is the line between two points. So, drawing a Read More
Vibration Isolators

There are a number of vibration sources throughout the world. In most cases, these movements have undesirable effects on things used in daily life, such as buildings and vehicles. Vibration isolators reduce or eliminate the effects of vibrations on equipment and structures. These devices are commonly referred to as shock mounts, snubbers, machine mounts, and Faraday cages (in the semiconductor industry). Vibration isolators are made from various materials, depending on their function. Some of these materials include rubber, metal alloys, neoprene, and fiberglass. How do Vibration Isolators Work? Most vibration Read More
What is an Accelerometer?

Accelerometers are electromechanical devices that measure the force of acceleration. This force can be dynamic (i.e the accelerometer being moved or vibrations cause it) or static (such as the force of gravity) in nature. The devices have a number of uses, such as determining the device angle or aspect with respect to the Earth, determining whether a vehicle or other structure is moving horizontally, and vibration measurement. How are Accelerometers Used? Accelerometers help engineers and mechanics determine problems in vehicle engines through vibration analysis. They determine existing damage as well Read More
Ellipsometry
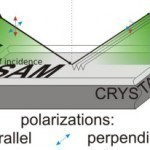
Ellipsometry is an optical technique used to investigate thin films’ dielectric properties (complex refractive index or dielectric function). Ellipsometry has many different applications. It can be used in semiconductor physics, microelectronics, biology, basic research, and industrial applications. This measurement technique’s sensitivity gives it an unequaled ability for measuring thin film. When analyzing the polarization of light, ellipsometry provides information about layers that are much thinner than probing light’s wavelength. It can even go down to a single atomic layer and can also probe the refractive index and/or dielectric function tensor. Read More
What is a Peltier Cooler?

A Peltier Cooler or Peltier Heat Pump is a type of refrigerator that has no moving parts and is capable of transferring heat to either side of itself. Peltier Coolers are advantageous as they are solid state devices and only require a DC electrical current in order to cool an object or area. A Peltier Cooler is the opposite of a thermoelectric generator as it converts electricity into a temperature difference, rather than a temperature difference into electricity. Peltier Coolers are used for various purposes and can be seen in Read More
How Do X-Rays Work?
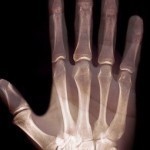
An X-ray is an electromagnetic wave that has a shorter wavelength than visible light and is created when an electrical current passes through an x-ray tube. When the current passes through the tube, the resulting radiation beam is an x-ray. This beam can penetrate objects or materials that consist of light atoms, but objects made of heavy atoms will absorb it. This quality makes X-rays useful for detecting bone fractures and for studying the structure of materials. When were X-Rays Discovered? German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen was the first scientist to Read More
What is a Dynamometer?

A dynamometer is a device that measures the power, torque, or force that is being applied to a system or object. Dynamometers also measure how much power, torque, or force is required to perform work within a system. They are used in industrial equipment in order to calculate the amount of power required to operate a machine and moderate power levels in order to prevent accidents that result from too much torque, pressure, or force being applied to an object. How Dynamometers Work Dynamometers work in several ways. The most Read More
High Temperature Superconductors
The primary problem with the current use of electricity is that of electrical resistance. In broad terms, this refers to the "opposition" of the materials to the electricity passing through them. Almost all materials now used to conduct electricity exhibit resistance to some degree or another. This results in some loss in the electrical power distributed to consumers and users – either in terms of generating heat (which is the reason for cooling fans and "heat sinks" in many electrical appliances – they are needed to dissipate the heat created Read More
Ultrasonic Welder

An ultrasonic welder is a device that uses ultrasonic sound waves to weld metals and plastics. Although most people are unaware, ultrasonic welders are often used to produce, seal, and package many everyday items such as milk jugs, butane lighters, and soda cans. Many different industries, such as the aerospace, automotive, medical, computer, and electrical industries use ultrasonic welders for a wide variety of applications such as cutting, sealing, joining, packaging, or bending. Ultrasonic welding is most often used when an object is too small or delicate to undergo more Read More


Share on: