Telephone Voltage
Telephone voltage is actually related to the physical distance at which you can operate the telephone. If the voltage is high, it can signal to great distance. However, higher voltage carries certain risks.
48 V is a compromise between distance and safety. 50-52 V is used in central office common batteries, but designations and documents still use the nominal voltage.
In the 20th century, some rural areas in theU.S. used range extenders. They operated at 130 V. The goal was to achieve reliable signaling. Some of the systems used in rural areas were created to use range extenders internally. This means that range extenders could share several extenders among numerous lines, whereas other lines used an external appliqué (for each line) as an extender.
Originally, engineers used positive voltage, but with this system, the copper wires used to age quickly, as a result of electrolysis. They started using negative voltage, which helped protecting the copper from corrosion (cathodic protection).
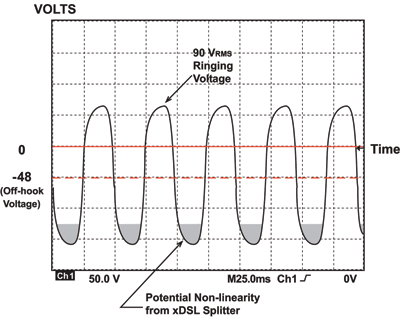
According to AT&T, the ringing signal is an 88v 20Hz A.C. signal superimposed on 48v nominal D.C. supervisory voltage. However, the actual ringing signal used can and does vary greatly from one location to another.
The frequency of the AC signal is normally between 15 and 70Hz.
The interval between ringing signals is normally four seconds.


Comments - One Response to “Telephone Voltage”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.