Understanding Proxy Server
Proxy Server Overview
Proxy Server enables you to connect the private network or LAN to a public network such as the Internet, by acting as a gateway for internal client computers to the Internet. Proxy Server is a secure gateway which you can use to provide Internet connectivity for IP and IPX based networks. A gateway is a computer that makes it possible for two networks to communicate.
Proxy Server services should run on one computer to which both the private network and the public network is connected to. The computer running the Proxy Server services should have two network interfaces:
- A network interface that points to the public network.
- A network interface that points to the private network.
The operations of Proxy Server are transparent to client computers. This means that users are not aware that the Proxy Server is actually requesting content on the Internet on their behalf. Users only becomes aware of the presence of the Proxy Server when they request content that the Proxy Server has been configured to disallow. The Web server servicing the request for content processes these requests as if they originated from the actual users.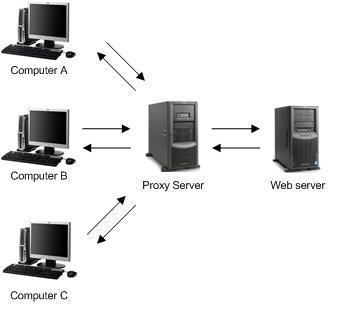
Microsoft Proxy Server version 2.0 is an extensible firewall and content cache server. Proxy Server version 2.0 provides Internet security, faster Internet access, caching services and improves network response time. Proxy Server can locally cache Internet sites and files which are frequently requested. These requests are then serviced from the local cache. This leads to an increase in Internet performance. Proxy Server can provide network address translation to support private IP addressing. Proxy Server includes a number of services which administrators can utilize to manage and control connections to the Internet. You can limit the Web sites that users can access. You can also prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing the private network.
When Proxy Server is used as a gateway to the Internet, unauthorized Internet users are basically prevented from accessing the private network. This is due to Proxy Server being the barrier between the private network and public network – requests for content on the Internet is allowed, and unauthorized access from the Internet is blocked. You can however use the reverse proxy feature to provide Internet users with the ability to access Web sites on the network via the Proxy Server.
The services provided by Proxy Server are listed here. These services are discussed in finer detail in another section of this Article.
- Packet filtering router.
- Web Proxy.
- Winsock Proxy.
- Socks Proxy.
- Reverse Web Proxy.
The main benefits and features of Proxy Server are summarized here:
- Proxy Server provides a secure gateway to the Internet. It acts as the control point between the private network and the Internet. Only a single secure gateway or control point needs to be managed, and you can also control the flow of traffic at the Proxy Server.
- Numerous users can utilize the single Internet connection provided by Proxy Server. This leads to cost savings with regard to modems, telephone lines, and so forth.
- The IP addresses utilized on the private network are not revealed on the Internet. When users on the private network request content on the Internet, the public IP address of the Proxy Server is used, and not the private IP addresses. In this way, private IP addresses are never visible on the Internet or used on the Internet.
- Because of the Proxy Server has two network interface cards, the LAN is secured from unauthorized users attempting to access the private network. Only one point of contact exists between the private network and the Internet.
- Proxy Server 2.0 provides a dynamic packet filtering feature that enables you to block specific packet types through ports.
- Proxy Server can locally cache Internet sites and files which are frequently requested. Subsequent requests for these Internet sites are then serviced from the local cache. Cached information is accessed by users from a location on the Local Area Network (LAN). This means that bandwidth utilization to the Internet ends up being lowered because cached information does not need to be downloaded from the Internet. All of this leads to an improvement in the service experienced by users.
- Proxy Server, by default, provides network address translation between the private network and the Internet. This basically means that Proxy Server supports private IP addressing schemes and public addressing.
- Proxy Server also provides a feature called proxy arrays. A proxy array is a solution whereby one or multiple proxy servers operate as a single cache for client requests. Benefits provided by the proxy array feature include scalable performance, and fault tolerance.
- Clients running WinSock and SOCKS applications can use TCP/IP or IPX/SPX to access the Internet via Proxy Server.
- Proxy Server also includes Web publishing support. You can utilize the reverse proxy feature to provide Internet users with the ability to access Web servers hosted on the network through the Proxy Server. Reverse hosting takes place when multiple Web servers are able to publish to the Internet.
- Access to the Internet can be based on users, or groups of users. Proxy Server can provide different types of access to the Internet, based on each group of users.
- You can limit the Web sites that users can access.
- Internet usage for each user can be tracked and logged.
Web Proxy Service Overview
The Web Proxy service supports Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTT), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Gopher communications from the private network to the Internet. The Web Proxy service supports requests to the Internet from CERN-compliant browsers. This includes browsers such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
The Web Proxy service performs server and client functions:
- Server functions performed include receiving requests for content on the Internet from internal network clients.
- Client functions include requesting content from Web servers on the Internet to service internal network clients’ requests.
The features provided by the Web Proxy service are:
- Supports Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Gopher communications from the private network to the Internet.
- For Web browsers that support Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication, encrypted logon is supported.
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) support on the Local Area Network (LAN).
- Support for the commonly used client operating systems and hardware platforms.
- Support for data encryption through Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) tunneling.
- Numerous computers can utilize a single IP address.
- CERN proxy compliance.
- Support for user level security for application protocols.
- Support for disk caching.
- Support for caching of HTTP and FTP objects.
- Internet requests of clients can be logged.
- You can use the Internet Service Manager tool to manage Proxy Server services and Internet Information Server (IIS).
The two important Web Proxy service components are:
- Proxy Server Internet Server Application Programming Interface (ISAPI) filter: The Proxy Server ISAPI filter checks each request received to determine whether the request is a standard HTTP request or a CERN proxy request. The Proxy Server ISAPI filter is called whenever a request is received. The identity of the resource requested is irrelevant.
The Proxy Server ISAPI filter can perform a number of operations on requests received by a Web server:
- Authenticate requests.
- Monitor and log requests.
- Modify, or add information to requests.
- Redirect requests.
When the Proxy Server ISAPI filter examines requests, it performs either of the following actions, based on the type of request received:
- If the request received is a CERN proxy request that has a complete URL (protocol and domain name); then the Proxy Server ISAPI filter adds information so that it can be forwarded to the Proxy ISAPI application for further processing.
- If the request received is a standard HTTP request that includes no protocol and domain name, then the Web server processes the request. The Proxy Server ISAPI filter inserts no additional information for these types of request.
- Proxy Server ISAPI application interface: The Proxy Server ISAPI application is only called when a request indicates a particular application. A new process is not started for each request received.
When ISAPI requests are received, the Proxy Server ISAPI application performs the following process:
- Client authentication occurs.
- A domain filter check is performed.
- Checks whether the resource exists in the cache. If it does exist in the cache and if the cached copy is current, the resource is retrieved from the cache and is then returned to the client.
- If the request was not found in the cache, the resource is obtained from the Internet and returned to the client. The information is then cached.
When HTTP requests are received, the Proxy Server ISAPI application performs the following process
- The domain name is resolved into an IP address.
- A connection is established with the Internet site.
- The request is forwarded to the Internet site.
- A response header is received from the Internet site.
- The information is then read.
- The information is forwarded to the client. The information is then cached.
The Web Proxy service utilizes two types of caching methods to cache HTTP and FTP objects:
- Passive Caching: Here, Proxy Server stores objects in the Proxy Server cache with each object obtaining a Time To Live (TTL) value. Before Proxy Server forwards requests to the Internet, it first checks the Proxy Server cache to determine if the request can be serviced from there.When the TTL of a cached object has not expired, requests are serviced from the Proxy Server cache. When the TTL of a cached object expires, the subsequent request for the object will result in the object being retrieved from the Internet, and returned to the client. The object is then placed in the Proxy Server cache once more, together with a TTL value. When the Proxy Server cache becomes full, Proxy Server removes objects from the cache, based on a combination of factors: object size, object age, and object popularity
- Active Caching: Active caching works together with passive caching. With active caching, Proxy Server automatically generates requests for specific objects in the Proxy Server cache so that frequently requested objects remain cached.
- Object popularity:
- Time To Live (TTL) value of objects.
- Server load determines the level of active caching performed.
Proxy Server determines which objects should be flagged for active caching by considering the following:
Winsock Proxy Service Overview
Winsock Proxy is a circuit-level gateway that enables Windows based clients running TCP/IP or IPX to access resources on the public network. The WinSock Proxy service provides client end and server end support for the common Internet applications which communicate via Windows Sockets. A Winsock Proxy Client has to be running on each computer though. The Winsock Proxy Client passes requests sent to the OSI Session layer to the Winsock Proxy Server. After the request is verified, it is sent to the Internet.
The features provided by the WinSock Proxy service are:
- Supports client computers running Microsoft Windows.
- Includes support for Windows Sockets compatible applications.
- All current Windows Sockets version 1.1 applications are supported.
- Includes support for both IPX/SPX and TCP/IP.
- Multiple computers can utilize a single IP address.
- Supports Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication between the client and server.
- Support for data encryption through Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) tunneling.
- Internet users are blocked from accessing the private network.
- Inbound and outbound access can be controlled, based on:
- Protocol.
- Port number.
- User/group.
- Access to Internet sites can be filtered, based on:
- Domain name.
- IP address.
- Subnet mask.
- Internet requests of clients can be logged.
- You can use the Internet Service Manager tool to manage Proxy Server services and Internet Information Server (IIS).
Socks Proxy Service Overview
SOCKS is basically a protocol that operates as a proxy. The Socks Proxy is a cross-platform mechanism that establishes a secure proxy data channel between client and server computers. The Socks Proxy service enables both Windows based clients and non-Windows based clients to access the Internet. The Socks Proxy service supports SOCKS version 4.3a.
The features provided by the Socks Proxy service are:
- Supports all commonly used client operating systems and hardware platforms:
- Windows.
- UNIX.
- Macintosh.
- Supports TCP/IP on private internal networks.
- Includes support for the Identification Protocol.
- The SOCKS standard configuration file is supported.
- IP authentication is utilized to create a communication channel.
- Requests of clients can be logged.
Packet Filtering
Proxy Server supports packet filtering, even though the capability is disabled by default when Proxy Server is installed. The packet filtering capabilities of Proxy Server allow you to control the traffic which passes to and from the Proxy Server.
You should use the packet filtering features of Proxy Server to control the flow of traffic between connection points to the following locations:
- Internet
- WAN connections.
- LAN connections
Through packet filtering, you can control outgoing traffic flows, allow specific incoming traffic flows, and block all other incoming traffic.
Packet filtering can be used to:
- Authenticate client requests.
- Control traffic flowing over the Proxy Server.
- Examine packet before the packets are passed to an application or higher protocols.
- Allow packets intended for specific services on the Proxy Server.
- Block packets intended for specific services on the Proxy Server.
- Configure that an alert be sent when suspicious activities occur or when packets are dropped. The alert can take the following forms:
- Written to the system event log.
- An e-mail message sent to an administrator.
- Both of these forms.
To support packet filters, the Proxy Server must have two NICs installed.
The types of packet filtering modes supported by Proxy Server are:
- Dynamic packet filtering: With dynamic packet filtering, the following occurs:
- Packets are automatically blocked from reaching specific services running on the Proxy Server.
- Ports are automatically opened and closed for transmitting, receiving, or for both of these operations by the Web Proxy, WinSock Proxy, and Socks Proxy services of Proxy Server.
- Ports are closed immediately after any one of the Proxy Server services ends a connection. This in turn minimizes the number of open ports, and decreases the time duration for which ports remain open.
- Static packet filtering: Administrators can also manually configure static packet filters. This is typically necessary when applications that access the Internet are hosted on the same computer hosting Proxy Server.
When using Proxy Server to provide Internet connectivity, you should implement Proxy Server packet filters to protect network resources in the private network from unauthorized access. When packet filters are used to protect private network resources, you can restrict traffic based on a combination of IP header information.
The criteria that you can include in packet filters are listed here:
- Direction; this is the direction of IP traffic in relation to the Proxy Server network interface. You should restrict the inbound traffic on the interface of the Proxy Server that is connected to the Internet
- Protocol ID; this is the IP ID for inbound traffic. You can also filter traffic by protocol ID, according to applications and services.
- Local Port; this is the TCP port number or UDP port number in the private network. When defining inbound traffic, local port pertains to destination port number. You can define one port number or a range of port numbers.
- Remote Port; this is the TCP port number or UDP port number on the Internet. When defining inbound traffic, local port pertains to source port number. You can define one port number or a range of port numbers.
- Local host IP address; this is the IP address of a computer residing on the private network, and is usually the Proxy Server interface’s IP address that is connected to the Internet. Any IP address on the private network can be specified.
- Remote host IP address; this is the IP address of a computer residing on the Internet. Any IP address on the Internet can be specified.
To restrict users on the private network from accessing resources on the Internet, you can use either of the methods listed here. When restricting access to resources hosted on the Internet, you essentially have to restrict Proxy Server outbound traffic:
- Packet filters: The methods used to restrict inbound and outbound traffic are the same, except for the direction specified in the packet filter.
- Domain filters: You can use domain filters to restrict Internet access to only certain IP addresses or FQDNs. In a domain filter, you can include a number of Internet sites and then define the action that the domain filter should take when a request is received for one of these sites:
- Reject packets for these specific Internet sites and forward all other packets.
- Forward packets to these specific Internet sites and reject all other packets.
- IP address – either a single computer or the IP address of a cluster. Traffic can be restricted between the private network and this particular IP address.
- IP address range – multiple computers. Traffic can be restricted between the private network and IP addresses within the IP address range.
- FQDN – you can forward packets for the FQDN or you can reject packets intended for the FQDN.
The criteria you can include in a domain filter are listed here:
- User account authentication: You can utilize Proxy Server user authentication to specify Internet access, based on user account. Proxy Server access can be specified to:
- An Active Directory user or group account. When you allow access to the Proxy Server for a group, all users residing in that particular group are allowed to access the Proxy Server.
- A user or group account in a member server.
Reverse Web Proxy Service Overview
The Reverse Web Proxy Service of Proxy Server allows incoming requests to be forwarded to an internal Web server, or internal Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP) server. This feature enables internally hosted Web servers to be accessed from public networks.
To enable internal Web servers to be accessed from public networks, you can use either of the following methods:
- You can locate the Web server on the public side of the firewall. The main disadvantage of this design is that the Web server is fully exposed to the Internet, and is therefore vulnerable to attacks from hackers.
- You can locate the Web server on the private network and then open a hole in the firewall so that all HTTP requests from the Internet can access the Web server. This design still leaves the Web server exposed to the Internet. In addition to this, the hole created in the firewall can be exploited by network attackers.
- Another method you can use is to reverse-host the Web site. Here, the Proxy Server exists between the Internet users and the Web server located on the private network. All requests from users on the Internet are sent to the Proxy Server’s public interface. From here, the requests are forwarded by the Proxy server to the Web server on the private network. The Web server is therefore not directly accessed by any users on the public network. With reverse proxy, additional Proxy Server features, such as caching, can be used.


Comments - One Response to “Understanding Proxy Server”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.