Virtual Machine
A virtual machine is a software-based replica of a physical machine such as a computer. A virtual machine is entirely independent from any physical hardware and can only use resources that have been added to the virtual machine. There are two types of virtual machines: system virtual machines and process virtual machines. System virtual machines contain all of the standard features that would be found in an operating system while process virtual machines are designed to carry out a specific function and are made to mimic a specific program.
How Does A Virtual Machine Work
A virtual machine is made up of a programming language within a programming language. The set of code that makes up the virtual machine keeps track of all calculations, actions, and functions that are performed while the virtual machine is being used. The difference between a physical machine and a virtual machine is that a physical machine keeps a permanent or semi-permanent memory of everything that happens while a virtual machine only holds this information as temporary memory and dumps it when the session is closed.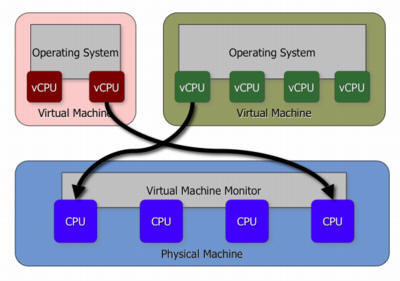
Isolation
Virtual machines are often used in order to isolate one application from another. This is because applications often interfere with each other and can cause problems. For example, if a user installs an external wireless adapter and tries to use that adapter’s connection manager, it will conflict with Windows’ built-in connect manager and will cause it to stop working. While only one connection manager is needed to do the task, the user may wish to interact with one while the other is running. A solution to this situation would be to run the external application in a virtual machine while Windows runs its own network connection manager.
Portability
Virtual machines are also very portable and can be moved from one physical machine to another. This is because virtual machines store their information in a single file on the physical machine. This means that in order to move a virtual machine from one physical machine to another, the user simply has to transfer to virtual machine disk file and several configuration files to the other physical machine. In addition to moving a virtual machine from one physical machine to another, users also have the ability to create multiple virtual machines on the same physical machine.
Testing
Virtual machines are often used to test situations. This is because virtual machines are not real and any problem that may occur in a virtual machine does not affect the physical machine that it is hosted on. This is great for software designers because they can test flaws in their application and try to fix them without causing any harm to the physical machine or to their program. Most virtual machines also have rollback features that allow the user to reverse their last action instead of having to start all over.
Consolidation
Virtual machines increase consolidation among applications because they allow for many different applications to be run simultaneously and use up very little resources from the physical machine that they are hosted on. System virtual machines in particular are great for consolidation because they can replicate entire operating systems and perform any feature that an operating system could but without the drawbacks and restrictions of a physical machine.


Comments - No Responses to “Virtual Machine”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.