An electrical shunt is a component used to transfer currents away from parts of a circuit. Components used as shunts include the resistor, capacitor, diode, and gas discharge tube. The main uses for electrical shunts are to reduce current load in meters, filter out high frequencies, and protect circuits from surges. The term shunt is also used in other fields, such as medicine, to describe non-electrical devices that perform a bypass function. Shunt Types Shunt resistors, also called bypass resistors, are large metal components with very low resistance. They look Read More
Thyristor

A thyristor is a solid state semiconductor device that consists of four alternating layers of N-type and P-type material. Many sources consider thyristors to be the same as Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs). In some cases they are defined as a large group of devices – the eligibility criterion being that the device should consist of a minimum of 4 layers of alternating N and P-type material. A thyristor functions as a bistable switch, which means that it starts conducting when its gate receives a pulse of current. It conducts until the Read More
GPS (Global Positioning System)

GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It refers to a system of satellites that constantly transmit a signal, and a GPS terminal that picks up those signals and calculates its position on Earth by measuring the distance between itself and two or more GPS satellites (by measuring the time it takes to receive the signals). How to Use GPS GPS operates using trilateration. Trilateration is the process of determining the position of an unknown point by measuring the lengths of the sides of an imaginary triangle between the unknown point Read More
Internet Repeater

An Internet repeater is a device that allows amateur radio operators to communicate with each other over the Internet, much like how VoIP software allows telephone operators to communicate with each other over the Internet. Internet repeaters should not be confused with wireless repeaters, which allow users to extend the range of a wireless network. While many amateur radio hosts simply use their radio equipment to stream live radio shows on the Internet, Internet repeaters also allow radio operators to control remote radio locations, such as antennas and other broadcast Read More
How GPS Tracking Works
GPS – A Short Introduction GPS, which stands for Global Positioning System, is a satellite navigation system that can ascertain the latitude and longitude of a GPS receiver device on the Earth. The GPS consists of more than two dozen global positioning satellites orbiting the earth. Each satellite transmits radio signals, which can help determine the location, speed and direction of travel of users equipped with GPS receivers. To ensure that the whole world is covered by the constellation of the GPS satellites, they are so arranged that four satellites Read More
L band

L band is a fequency range between 390MHz and 1.55GHz which is used for satellite communications and for terrestrial communications between satellite equipment. The high frequencies utilized by C band, Ku band, and Ka band would suffer from high signal loss when transported over a copper coax cable such as an Intra-Facility Link. An LNB is used to convert these higher frequency bands to L band, which can be transmitted over the IFL and processed by the IDU. Some satellites transmit on L band, such as GPS satellites.
TRIAC

A TRIAC is used in AC power control applications in order to switch high voltages over both parts of the AC waveform. As a result, TRIAC circuits are used in a number of applications that require power switching. The TRIAC was developed after the thyristor, which controls AC current over one half of the cycle. The TRIAC circuit can be visualized as two thyristors that are opposite, parallel, and have the two gates connected together with one device’s anode connected to another’s cathode. A common household device that uses the Read More
Symbol Rate
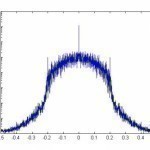
The symbol rate is the rate of state changes on a communications circuit. If a circuit can carry two tones per second, the circuit has a symbol rate of two. Circuits then use different modulation techniques to carry multiple bits per symbol. If the circuit is limited to two different tones, the first tone can represent a 0 and the second tone can represent a 1. In this circuit, the symbol rate is the same as the bit rate. If the circuit can carry four different tones, then the tones Read More
Nixie Tube
The Nixie tube, also called a counting tube, is a gas discharge tube used to display information. It is the predecessor of the light emitting diode and the liquid crystal display, both of which use less power and last longer than the Nixie tube. Although they are still made today, Nixie tubes have largely disappeared from modern electronics. History The idea of using a gas discharge to display information first appeared in the 1920s, but it wasn't until the 1950s that Nixie tubes became widespread. The term is actually a Read More
MS Connectors
MIL-C-5015, now known popularly as MS connectors, are multi-pin, highly durable connectors that were originally invented for use in military applications. They have a variety of features that makes them easy to use for nearly any application and are often found in a variety of advanced, high power, heavy duty devices in the industrial world. MS connectors are a type of circular threading connector that requires no tools to assemble. Installation can be done by simply the barrel into the receptacle and turning in the proper direction. This ease of Read More


Share on: