An inductor is a conducting coil, wrapped around a core, that creates inductance when an alternating current flows through it. Inductors are used to impede the flow of current in a circuit. The conductor is usually thin magnet wire, and the core is usually air or steel. Working of an Inductor When the alternating current flows through an inductor, it creates an electromagnetic field. The strength of this field depends on number of coils, the coil diameter and the permeability of the core material. Steel has a much higher permeability Read More
Multimeter
A multimeter combines several electrical meters into one hand-held unit. Basic multimeter models measure voltage, current, and resistance. Advanced models also measure temperature, inductance, capacitance, duty cycle, and frequency. They can also test diodes and transistors. Some even work as an oscilloscope. The two main types of multimeters are digital and analogue. Parts of a Multimeter A multimeter has a display, terminals, probes, and a dial to select various measurement ranges. A digital multimeter has a numeric digital display, while an analog has a dial display. Inside a multimeter, the Read More
How to Read Resistor Color Code

Resistors can come in different sizes and shapes allowing for different voltages to go through it. However, unless the size of the resistor is large, the code is rarely written on it because it would require very tiny markings. Therefore, a system was developed to use colors to determine the resistor code. In other words, by using different colors, an average user can determine exactly what the Ohms are for the resistor. Reading Resistor Code Count the number of color bands on the resistor. For resistors with a tolerance anywhere Read More
Laser Diode
A laser diode is a small device that is similar in construction and appearance to a light emitting diode (LED). The main difference is that a laser diode produces coherent laser light while an LED produces incoherent light. Ever since they were first invented in 1962, millions of laser diodes have been used in a wide range of consumer and industrial products. History The first laser diode was invented by a team of researchers at General Electric in 1962 but many other research teams also contributed to their initial development. Read More
What is a Loop Antenna?

A loop antenna is one that is designed to receive radio signals more efficiently than other antennas. Loop antennas are considered more efficient than others because they are mobile, work with a wide range of frequencies, and use less electricity. A loop antenna’s performance is entirely dependent on its construction and placement, although other factors may also play a role. Loop antennas locate areas with ideal signal strength, and improve signal quality and communication. How Loop Antennas Work A loop antenna is made of a loop of copper or another Read More
What is a Capacitor Bank?

A Capacitor Bank is a group of several capacitors of the same rating that are connected in series or parallel with each other to store electrical energy . The resulting bank is then used to counteract or correct a power factor lag or phase shift in an alternative current (AC) power supply. They can also be used in a direct current (DC) power supply to increase the ripple current capacity of the power supply or to increase the overall amount of stored energy. What Does a Capacitor Bank Work? Capacitor banks Read More
What is a Decoupling Capacitor?
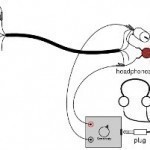
A decoupling capacitor (bypass capacitor) is a device that separates current and voltage levels from two separate sections of the same electronic device. Decoupling capacitors are useful in situations that require an electronic device to fluctuate current or voltage levels without straining the power supply. Decoupling capacitors can be used in electronic devices that have frequencies between several hundred KHz and several hundred MHz, but are not useful in devices that have frequencies above or below this range. How a Decoupling Capacitor Works A decoupling capacitor serves as a Read More
What Are Op-Amp Circuits?
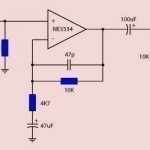
An op-amp (operational amplifier) circuit is a device that amplifies the difference between two or more input voltages. Op-amp circuits are the most widely used electronic devices in the world due to their integration in a wide variety of electronic goods. There are many op-amp circuit variations available and several types of differential amplifiers that are made by using several op-amps together. How Op Amp Circuits Work Op-amp circuits take a voltage from two or more inputs, amplify it, and usually feed it back to the voltage source. Op-amp circuits Read More
LNB (Low Noise Block)

An LNB (Low Noise Block aka LNC- Low Noise Converter) is used for communications (broadcast) satellite reception. The LNB is usually affixed either in or on the satellite dish. The LNB’s purpose is to utilize the super heterodyne effect and amplify and convert a wide block (band) of frequencies. This helps compensate the signal loss associated with typical coaxial cable at relatively high frequencies. The term ‘low noise’ relates to the quality of the 1st stage input amplifier transistor, measured in either called Noise Temperature units, Noise Figure units, or Read More
TV-GPS Technology
TV-GPS is a technology from Rosum Corporation of California. Basically, it is a GPS tracking technology that makes use of television broadcasting signals to intensify or strengthen GPS signals. It is slated for use in urban areas where most people own a television (so the TV broadcasting signals are extremely strong) and where the regular GPS monitoring or tracking is rendered ineffectual because of great interference from electromagnetic noise and obstruction from concrete skyscrapers. Components of a TV-GPS System A TV-GPS system needs a device with a Rosum TV Measurement Read More


Share on: