Ham Radio Software, also known as Amateur Radio Software, refers to computer programs designed exclusively for ham radio equipment. Once thought to be a means of communication between radio enthusiasts, ham radio now coexists with software including data and contest loggers, log books, Morse code tutors, and antenna design aids. In the 21st century there are several software companies that have developed programs specifically for amateur radio enthusiasts. Logging Software: Freedom and Functionality Most ham radio software programs pay acute attention to the logging features of their software due to Read More
Plastic Electronics
Plastic electronics is an offshoot of electronics which focuses on devices made from conductive plastics – otherwise known as organic polymers – rather than silicon. Manufacturing Plastic Electronics The "heart" of modern electronics are microchips – circuits and wiring "diagrams" are designed and micro-miniaturized to the point that thousands or even millions of circuits are contained in a one-inch square chip which is "burned" (or etched) onto ultra-thin inorganic materials like refined silicon using very high temperatures. Plastic electronics, on the other hand, follow a different manufacturing process. The process Read More
Whole House Surge Protector
As the average home continues to add electronic devices of all types, it is becoming increasing necessary for the home to be protected by a whole house surge protector. Stray electric charges can enter the home and damage or destroy expensive electronic equipment. In many cases, these surges of electric power can even lead to fire, destroying the entire home. Individual surge protection devices are mandated in most communities, but a whole house unit may be needed to protect against catastrophic damage. So You Think You Already Have a Surge Read More
Ultrasonic Sensors

An ultrasonic sensor is a device that works in much the same way as RADAR and SONAR. In fact, ultrasonic sensors mimic bats and other animals’ natural ability to use ultrasonic frequencies for navigation. Ultrasonic sensors broadcast a powerful, ultrasonic frequency, then detect the ultrasonic sound waves as they bounce off of objects and return to the sensor. They are almost always used to measure speed or direction and are very efficient at determining position. How Ultrasonic Sensors Work Ultrasonic sensors depend on two separate devices: an ultrasonic transducer and Read More
Feedhorn

The feedhorn is the part of a satellite dish system which gathers the reflected signal from the dish and focuses it towards the LNB. It is a type of horn antenna that is deployed to convey radio signals between the transceiver and the reflector antenna. Horn antennas basically effect a transition between waves propagating through a transmission line like a waveguide and the waves propagating in free space. The shapes could be various, based on the final purpose of regulating some of the fundamental properties of gain, radiation pattern and Read More
Azimuth
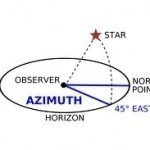
Azimuth is a measurement at an angle used in the spherical coordinate system. To find a point of interest, the observer creates a vector that is then projected in a perpendicular fashion onto a reference plane. The resulting angle between the projected vector and the reference vector located on the reference plane is the azimuth. It is the direction on the reference plane that is used to determine where the point of interest lies in the spherical coordinate system. A common use of the azimuth measurement is to find the Read More
Heterodyne
A heterodyne is a circuit that transfers a signal from one carrier wave to another with a different frequency. It mixes the input signal with a wave generated by an oscillator to create two new signals, called beats. While heterodyning is a simple process governed by the laws of trigonometry, most heterodynes are complex devices with several filters and amplifiers. Heterodyne Beats A beat is a signal produced by two input signals with different frequencies. A heterodyne produces two beats, one with a frequency that is the sum of the Read More
Baseband
Generally, a transmission signal contains more than a single frequency. This is to say that there might be several different frequencies linked together or else superimposed on each other. This is just the way all telecommunication systems function. For example, with today's communication technology it is virtually impossible to send low frequencies without experiencing any distortion. In fact, when low frequencies are sent the distortion is frequently so severe that the signal cannot even be used. So, what is to be done with the low frequencies to make them usable? Read More
FRS (Family Radio Service)
FRS (Family Radio Service) is an unlicensed service. FRS (Family Radio Service) consists of 14 UHF channels on FM. FRS Channel 1 is unofficially used as a common call channel. FRS (Family Radio Service) shares channels 1 through 7 with GMRS, and many FRS radios are also GMRS radios. The maximum allowable power for a FRS (Family Radio Service) radio is .5 watts. GMRS radios are allowed to transmit on the channels they share with FRS at 5 watts, ten times the power of FRS radios. Unlike GMRS, repeaters are Read More
Ku Band

The Ku band (Kurtz-under band) is primarily used for satellite communications, particularly for editing and broadcasting satellite television. This band is split into multiple segments broken down into geographical regions, as the ITU (International Telecommunication Union) determines. The Ku band is a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies ranging from 11.7 to 12.7GHz. (downlink frequencies) and 14 to 14.5GHz (uplink frequencies). The most common Ku band digital reception format is DVB (main profile video format) vs the studio profile digital video format or the full-blown Read More


Share on: