NAT (Network Address Translation) is a technique for preserving scarce Internet IP addresses. Why NAT? The current Internet uses IP addresses in the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. A sample IP address might be 202.187.4.212. Because of the way these IP addresses are allocated, there started to be a shortage of available IP addresses. The current IP (Internet Protocol) revision in use on the Internet is IPv4. IPv6 is largely a response to this potential IP address shortage. Unfortunately, IPv6 is going to take decades to implement. A much quicker fix was needed, Read More
How to Use Ping to Test a Network
The following steps elaborate on how to use the Ping utility to perform progressively more distant tests on network connectivity. Ping the Loopback Address – Type Ping 127.0.0.1 Successfully pinging the loopback address verifies that TCP/IP is both installed and configured correctly on the local client. If the loopback test fails, it means IP stack is not answering. If any TCP drivers get corrupted, the network adapter is not functioning properly, or any other service is interrupting IP , then lack of response might occur. Open event viewer and look Read More
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
ICMP is the Internet Control Message Protocol. ICMP is a complementary protocol to IP (Internet Protocol). Like IP, ICMP resides on the Network Layer of the OSI Model. ICMP is designed for sending control and test messages across IP networks. Unlike the Transport Layer protocols TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) which operate on top of IP, ICMP exists alongside IP. The ability to understand ICMP is a requirement for any IP-compatible network device. However, many security devices such as firewalls block or disable all or part Read More
BOOTP
BOOTP is the Bootstrap Protocol. The BOOTP protocol is utilized by diskless workstations to gather configuration information from a network server. The information provided by the BOOTP protocol is: The IP address which should be utilized by the diskless workstation The IP address of a server which will provide an Operating System image for the diskless workstation The filename of an Operating System image which the diskless workstation should boot BOOTP workstations are identified by their MAC addresses. The BOOTP protocol utilizes UDP ports 67 and 68. Additional Reading on Read More
How to Set a Static IP
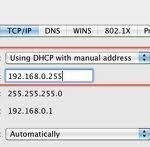
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier for any device that connects to the Internet. All computers, modems, routers, mobile devices, and even accessory items such as printers, scanners, and fax machines have an IP address. IP addresses are extremely common in the web design industry because every website must be associated with a specific server that is identified by its IP address. IP addresses are very important in the information technology era because without them, computers and other devices would not be able to find or access Read More
Routing

Routing is the process of moving packets through an internetwork, such as the Internet. Routing actually consists of two separate, but related, tasks: Defining paths for the transmission of packets through an internetwork. Forwarding packets based upon the defined paths. Routing takes place in IP networks, based on IP routing tables and its entries. The information in the IP routing tables is used by IP hosts to transfer data over the internetwork. Routers are devices operating at the network layer of the OSI model that use the IP routing tables to forward Read More
GBE (GigaBit Ethernet)
GBE stands for Gigabit Ethernet, which is a general term for a group of standards which allows for networking at speeds of up to one billion bits (one gigabit) per second between devices on a Local Area Network. Gigabit Ethernet can also be abbreviated as GbE or 1 GigE. Gigabit Ethernet is one of the latest implementations of the Ethernet standard, a frame-based computer networking technology originally developed at the prolific and creative Xerox Palo Alto Research Center in the 1970’s. The name is derived from the late 19th century Read More
What is a Zeroconf?
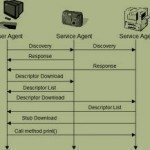
Zeroconf (zero configuration networking) refers to several protocols and techniques that are used together to create an IP (Internet Protocol) network with no special configuration servers or manual operator intervention. These networks allow novices to connect computers, network devices, scanners, and printers to create a functioning network without requiring manual configuration. Zeroconf does not require the user to set up Domain Name System services (DNS), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), or manually configure the computer’s network settings. The three primary technologies that comprise a zeroconf network are automatic resolution and Read More
Broadcast Domain
A broadcast domain is a logical part of a network (a network segment) in which any network equipment can transmit data directly to other equipment or device without going through a routing device (assuming the devices share the same subnet and use the same gateway; also, they must be in the same VLAN). A more specific broadcast domain definition is the area of the computer network that consists of every single computer or network equipment that can be reached directly by sending a simple frame to the data link layer’s Read More
Subnet Masks
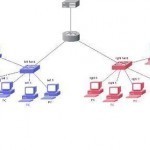
A subnet mask allows users to identify which part of an IP address is reserved for the network and which part is available for host use. By looking at the IP address alone, especially now with classless inter-domain routing, users cannot tell which part of the address is which. Adding the subnet mask or netmask gives users all the information needed to calculate network and host portions of the address with ease. In summary, knowing the subnet mask can allow users to easily calculate whether IP addresses are on the Read More


Share on: