Airborne Internet refers to installing a broadband network hub in an aircraft flying at 52,000 to 69,000 feet above sea level – high enough to be out of weather disturbances and way outside the flight envelope of commercial aircraft. The aircraft will provide Internet connection to places and establishments within its range. The Need for Airborne Internet Airborne Internet is seen as the perfect answer to the demand for fast, reliable access to the Internet as well as quick and easy file 'sharing.' Currently, the problem lies in the physical Read More
How to Set a Static IP
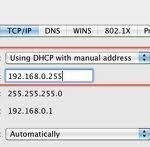
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier for any device that connects to the Internet. All computers, modems, routers, mobile devices, and even accessory items such as printers, scanners, and fax machines have an IP address. IP addresses are extremely common in the web design industry because every website must be associated with a specific server that is identified by its IP address. IP addresses are very important in the information technology era because without them, computers and other devices would not be able to find or access Read More
802.11a
802.11a is one of the many standards used for high speed wireless networks, usually referred to as Wifi. This standard was created by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) in 1999 and uses several different frequencies including 5.15-5.35/5.47-5.725/5.725-5.875 GHz to send and receive data from one electronic or computer device to another. There are many different standards of the 802.11 used today for wireless communication; the other popular standards include 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n. The standard 802.11a has been available for several years, but has not caught on Read More
Wireless Routers
A wireless router is a wireless device that connects one computer or a whole network to another computer or network. It is possible to have a wireless network in a home or office. Travelers definitely come across wireless networks at most international airports. A wireless router, which is responsible for sending information from one computer to another, powers a wireless network. The router help the user to share a single Internet connection between two or more computers, which can be on the same floor or even on different floors. Wireless Read More
How Do ADSL Microfilters Work?

ADSL Internet Access Asynchronous Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) is a broadband Internet option that is commonly available in many locations. Asynchronous only means that the download speeds and the upload speeds are different (with the upload speeds usually being significantly lower) and provides a fast option to browse the web. Internet access through ADSL requires one of three things. The first will be a dedicated phone line to access the ISP through the ADSL modem which some people do if they do not use a land based phone or simply purchase an Read More
MIC (Message Integrity Check)
MIC (Message Integrity Check) is part of a draft standard from IEEE 802.11i working group. The MIC (Message Integrity Check) is an additional 8 byte field which is placed between the data portion of an 802.11 (Wi-Fi) frame and the 4 byte ICV (Integrity Check Value). The MIC has a function very similar to the older ICV. However, the ICV only protects the packet payload. The MIC protects both the payload and the header. The algorithm which implements the MIC is known as Michael. Michael also implements a frame counter, Read More
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
Network management systems use SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) to communicate with network elements. For this to work, the network element must be equipped with an SNMP agent. Most professional grade network hardware comes with an SNMP agent built in. These agents must be enabled and configured to communicate with the network management system. Operating systems such as Unix and Windows can also be configured with SNMP agents. SNMP Messages Either the network management system (NMS) or the network element intitiates SNMP messages. An SNMP TRAP is a message that Read More
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
A WLAN is a sort of Local Area Network (LAN) that implements high frequency radio waves instead of wires to communicate and transmit data. It is a supple data communication method put into practice as an expansion to or as a substitute for, a typical wired LAN. An Access Point joins wired and wireless networks collectively and facilitates the transmission of data between wireless consumers and the wired network. Implementing several access points enhances overall system capability and scope. Wireless consumers can wander between different access points without disconnecting, like Read More
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line)
ADSL is the acronym for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. ADSL is a loose set of protocols that allows for high speed Internet access over normal copper telephone lines or what is more commonly known as POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service). This is possible because the signals are sent digitally instead of through analog waves. ADSL is known as asymmetric because the download and upload speeds are not symmetrical with download speeds being averagely faster than upload speeds. Upstream data speeds are lower because requests for web pages normally do not Read More
DNS Cache
DNS (Domain Name Server) is the web server used to resolve a website’s name to its Internet Protocol (IP) address. DNS servers across the Internet are either considered authoritative with regards to a website name and corresponding IP address or are required to verify the IP address with another DNS server that will in turn request verification from another DNS server if it is not the authoritative resource for the name resolution. As a result, Internet performance could be significantly impacted if there were not some method around the large Read More


Share on: