Every office and small business needs a method of running multiple communication programs such as conference calling, video conferencing, media distribution, instant messaging, and account management software. To perform these tasks, servers need the help of a SIP gateway to bridge the gap between data streams and the Internet. SIP gateways are also essential in VoIP networks as they allow for mutiple audio and video connections to take place at one time over the Internet. Moreover, using a SIP gateway is an affordable and efficient method of networking in and Read More
RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol)
RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol) is a protocol used in VoIP to manage QoS (Quality of Service). RSVP works by requesting that required bandwidth and latency be “reserved” for the VoIP telephone call by every network device between the two endpoints. RSVP is defined in RFC 2205: Resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP). RSVP is a unicast and multicast signaling protocol, designed to install and maintain reservation state information at each router along the path of a stream of data. The RSVP protocol is used by a host to request specific qualities of Read More
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)

VoIP (Voice over IP) includes communication protocols, technologies and techniques of transmission used for multimedia sessions and voice communication via IP networks. Other terms used synonymously with ‘Voice over IP’ include broadband phone, voice over broadband and Internet telephony. How Does VoIP Work? VoIP calls require media channel setup, analog voice signal digitalization, encoding, packeting and transmission of IP packets via packet-switched network. On the receiving end, there will also be packet-decoding, conversion of analog signals to digital signals, and IP packets reception. VoIP uses audio codecs that encode speech Read More
VoIP QoS

VoIP QoS (Voice over Internet Protocol Quality of Service) is used in VoIP services to determine a VoIP network’s overall performance and make changes to increase the customer satisfaction rate. QoS is used in other systems (like computer networks) as well, but is especially important in VoIP services because of the high demand for prompt, real-time voice packet delivery and call handling. VoIP QoS generally refers to the VoIP system’s bit rate, delay, and bit error rate and provides customers with a realistic idea of the VoIP network’s capabilities. How Read More
How to Get Free VoIP
Free VoIP calls are never completely free of cost. Often, the goal is not to achieve completely free calls to all destinations, but to use the VoIP operator that suits one’s needs best. Keeping that in mind, one will learn that most VoIP companies let users talk for free in their own network, but will charge for making calls outside their proprietary network. Companies offering free VoIP calls usually offer free calls inside their own network and towards other specially selected destinations. Using this tactic, users are drawn to make Read More
VoIP Codecs
A codec (Coder/Decoder) converts analog signals to a digital bitstream, and another identical codec at the far end of the communication converts the digital bitstream back into an analog signal. In the VoIP world, codecs are used to encode voice for transmission across IP networks. Codecs for VoIP use are also referred to as vocoders, for "voice encoders". Codecs generally provide a compression capability to save network bandwidth. Some codecs also support silence suppression, where silence is not encoded or transmitted. Codec Algorithm Bit Rate (Kbps) Comments ITU G.711 PCM Read More
What is a QSIG?
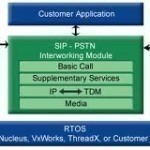
QSIG is a signaling protocol that is based on ISDN. It communicates signals between private branch exchanges (PBXs) within a Private Integrated Services Network (PISN) using the application-level ROSE and connection-level Q9.31 protocols. QSIG uses ISDN as the physical link layer in the exchanges and is often used in enterprise voice or integrated service networks. The Q reference point that the protocol derives its name from is the formal dividing or demarcation point between two PINXs (Private Integrated Network Exchanges). Who Invented the QSIG Protocol? ECMA International first created the Read More
How MagicJack Works

A MagicJack is a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) device that allows users to connect their home telephones to their computer in order to make free calls. A number of influential magazines such as the L.A. Times, CNBC, PC Magazine, and the New York Times strongly recommend MagicJack. It is, by far, the cheapest option for home telephone service in the U.S. While the Magic Jack requires an initial investment, there are never any monthly bills or call fees. How MagicJack Works A MagicJack has a USB attachment on one Read More
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is used to encapsulate VoIP data packets inside UDP packets. RTP is defined in RFC 3550 – RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications. RTP provides end-to-end network transport functions suitable for applications transmitting real-time data, such as audio, video or simulation data, over multicast or unicast network services. RTP does not address resource reservation and does not guarantee quality-of-service for real-time services. The data transport is augmented by a control protocol (RTCP) to allow monitoring of the data delivery in a manner scalable to large Read More
MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol) is a protocol used within a Voice over IP (VoIP) system. This internal protocol was primarily developed to address the demands of carrier-based IP telephone networks. MGCP is a complementary protocol for both H.323 and SIP, which was designed as an internal protocol between the Media Gateway Controller and the Media Gateway. In MGCP, an MGC primarily handles all the call processing by linking with the IP network through constant communications with an IP signaling device, for example an SIP Server or an H.323 gatekeeper. Read More


Share on: