Waste oil is the term used to refer to any petroleum-based/synthetic oil that is no longer considered usable. This may be due to the presence of excessive impurities, loss of the oil’s original properties, or just from the oil being over-exposed to the elements. A classic problem for society has been how to dispose of waste oil that is generated from commercial or residential use. Waste oil burners were initially designed to get rid of oil that was no longer usable, but can now be used to create heat or Read More
How a Nuclear Bomb Works
A nuclear bomb uses a nuclear reaction to generate energy (heat and radiated particles). The energy released is millions or in some cases billions of time stronger than TNT; the whole process is carried out in a very short time, providing huge destructive power. There are two types of nuclear reactions, fission and fusion. During fission the nucleus are broken apart and in fusion, they collapse one toward the other. Extremely heavy elements as uranium and plutonium are used in fission bombs and hydrogen (the lightest element) is used for Read More
What is an Acetylene Torch?
Acetylene is a hydrocarbon compound and is the simplest form of alkyne. Acetylene is colorless and extremely unstable in its pure form, which is why it is almost always mixed with other chemicals and handled as a solution. Acetylene was once the preferred gas in welding/cutting applications due to its ability to reach extremely high temperatures (3300 degrees Celsius/6000 degrees Fahrenheit) when mixed with oxygen. Acetylene produces the third hottest natural chemical flame, after cyanogen (4525 degrees Celsius) and dicyanoacetylene (4990 degrees Celsius). What is an Acetylene Torch? An acetylene Read More
How Hurricanes Form
Hurricanes are caused by immense low pressured formed over the warm oceans in the summer and early fall months. With this low pressure, water vapor is evaporated off of the ocean surface. This water vapor releases the latent heat of condensation which causes all of the water to begin forming into clouds. This condensation forms warmth around the surrounding air. Typically, a wind shear (change in wind speed or direction) causes the top of the tropical storm to blow off and destroys the fledgling hurricane. However, if there is a Read More
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the study of the nervous system as a whole. Someone who does neuroscience takes numerous different disciplines–psychology, computer science, mathematics, physics, philosophy and medicine to name a few–and bring them together with the understand of how the brain works. Traditionally, neuroscience was a branch of biology; however, because of a revolutionary change in how things are done, it's now evolved into a much larger network of understanding the brain's processes. Modern Day Neuroscience While in the past, neuroscience was all about understanding what neurons were, how to brain Read More
What is a Geosynchronous Orbit?

A geosynchronous orbit is when a satellite or other device’s orbit matches the Earth’s rotation so that the satellite travels around the Earth in a straight line and stays at the same point in the sky relative to the Earth. This means that as the Earth rotates, the satellites rotates around the Earth at the same speed so that its relative position never changes. Geosynchronous orbits are used for a number of purposes, including monitoring a specific region and communicating with Earth-based systems. Geosynchronous orbits include geostationary orbits, super-synchronous orbits, sub-synchronous orbits, and graveyard Read More
What is the Fifth State of Matter?
The fifth state of matter is actually the first phase of matter. It is called a Bose-Einstein Condensate. Matter in the fifth state is really slow moving and extremely condensed. It only exists at near absolute zero temperatures and is very fragile and unstable. It was discovered in 1995 by Eric Cornell and Carl Weiman through experimentation with rubidium, but the credit goes to Satyendra Nath Bose and Albert Einstein because they thought of the concept of this state of matter first. The only difference is that they did not have the tools available to Read More
What is Electrotherapy?
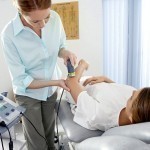
Electrotherapy is a medical technique in which an electric current is used to perform a wide variety of tasks associated with pain, neurological disorders, muscle-related conditions, and drug delivery. Electrotherapy includes a range of medical techniques, some of which are under much debate and criticism. While electrotherapy itself is an accepted form of medical treatment, electromagnetic therapy (a subset of electrotherapy) is usually discredited due to little evidence of either positive or negative effects. How Electrotherapy Works In electrotherapy, an electric current is applied directly to a muscle or tissue Read More
Oxygen Generators

An oxygen generator is a device that produces oxygen on demand, usually through the use of inorganic reactions. There are several types of oxygen generators but each depends on thermal reactions to produce oxygen. This causes the generator to become very hot, between 500 and 1,200 degrees Fahrenheit, and can present a serious fire hazard if mishandled. There have in fact been several situations in which people have died due to oxygen generator explosions. However, they are still used in various situations in which there is need for oxygen immediately, Read More
Speedometer Calibration
One of the most prominent gauges on an automobile’s dashboard is the speedometer. Its primary function is to give a visual indication of a vehicle’s speed in miles or kilometers (or both) per hour. Since the majority of these devices are still analog, they may require speedometer calibration when new tires are installed, major automotive repair work is completed, or it gives incorrect readings on a consistent basis. When Were Speedometers First Used? Automobile manufacturers first included Speedometers as standard equipment in 1910 as the need to limit drivers’ speeds Read More


Share on: