Holographic memory is a storage device that is being researched and slated as the storage device that will replace hard drives and DVDs in the future. It has the potential of storing up to 1 terabyte or one thousand gigabytes of data in a crystal the size of a sugar cube. Brief History of Holographic Memory Using holograms as memory storage was first proposed by Pieter Heerden in the 1960s. During the early 1970s, a group of scientists from TRCA laboratories succeeded in storing 500 holograms using an iron doped Read More
Clean Gas Induction
Clean gas induction, commonly referred to as CGI, is a technology found in specific types of engines to reduce harmful environmental emissions and improve fuel efficiency. Clean gas induction technology is found in specific types of engines including stratified charge engines and engines using Caterpillar ACERT technology. It should be noted that this technology is found in engines that run on either diesel or gas. As stated above, clean gas induction is used by both gasoline and diesel engines; however, the process of fuel induction is different for each kind Read More
Weather Modification Technology
Weather modification refers to willful manipulation of the climate or local weather. Research done in this field goes back to as far as the early 1940s when the US military experimented with cloud seeding to stimulate rain. Today, private corporations have joined the weather modification research effort to protect people, cities and assets from the damage extreme weather brings. Cloud Seeding History of Cloud Seeding Cloud seeding experiments started with the work of a scientist from General Electric named Vincent Schaefer who discovered that ice crystals can induce precipitation. Since Read More
What is a Fullerene?

A fullerene is a third form of the carbon molecule that falls in between graphite and diamond. It was named for Richard Buckminster Fuller, who was well known for geodesic dome designs whose appearance closely resembled spherical fullerenes. A Fullerene’s carbon atoms may be arranged in a cylindrical, ellipsoid, or spherical form. The spherical fullerenes are called “Buckyballs,” while the cylindrical ones are known as “Buckytubes” or “nanotubes.” When were Fullerenes Discovered? A group of researchers discovered fullerenes at Rice University while they were conducting laser spectroscopy experiments in September, Read More
How Wave Power Works
Wave power involves the ability to harness the power of the ocean's waves and use that power to generate electricity or do other types of useful work. Much like solar power, geothermal power, and wind power, wave power is known as a type of renewable energy source because nothing is consumed in the process. Also, wave power is often confused with tidal power, another type of power which is generated via the ocean. While wave power uses the actual surface waves which form in the ocean, tidal power takes advantage Read More
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution refers to the excessive, upsetting, and disruptive noise that machines or animals create. Aircraft, rail, automobiles, and construction sites cause the most noise pollution. Noise pollution occurs both indoors and outdoors. Other sources of noise pollution include fireworks, air horns, dogs, audio equipment, mechanical equipment, building or car alarms, and appliances. Noise pollution was largely ignored until the mid-1970's when the government started placing regulations on industries that significantly contributed to noise pollution. What Are the Effects of Noise Pollution on Human Health? Noise pollution can have a Read More
Laser Engraver
As its name suggests very clearly, laser engraving is the art of engraving or marking objects using one or multiple lasers. Considering the preciseness that is required with the engraving, the whole process is quite complex and technical, which often requires a computer. Therefore, as desired, the final engravings are done extremely precise at a very high rate. Most of the laser engraving done today is conducted by what is known as a laser engraving machine. This machine has three main parts to it: a laser, a surface, and a Read More
What is Photoelectron Spectroscopy?
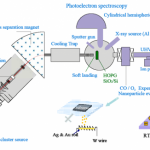
Photoelectron spectroscopy is the study of energy and how it relates to matter in terms of absorption and production. Photoelectron spectroscopy observes both wavelengths and frequencies and is used to view the physical composition of chemicals and solids. It is used in both analytical and physical chemistry and astronomy in order to study an object’s physical properties and velocity by measuring the amount of energy being transferred to and from the object. Specifically, photoelectron spectroscopy measures how the absorption of electromagnetic radiation affects the electrons it produced. How does Photoelectron Read More
How Overhead Projectors Work

Overhead projectors work with the help of transparencies. All data are printed on top of the transparencies. Before starting up, be sure to have a socket with live electricity where you can switch the overhead projector. The power buttons are usually made of first class plastic, the “click” sound is heard; it means it has been successfully put “on”. If the overhead projector is not working, try to push the button more slowly, and you can feel the “click”. Inside the overhead projector, usually it is like a television, but Read More
Fine Structure Constant

The Fine Structure Constant is a constant in theoretical physics that determines the strength of the interaction between two opposing electromagnetic waves. The Fine Structure Constant is used for a wide variety of purposes, but is entirely hypothetical and does not depend on any real units of physics. For example, the Fine Structure Constant can be used to determine the displacement of a beam of light as it comes in contact with a radio wave or vice versa. How the Fine Structure Constant Works The Fine Structure Constant is defined Read More


Share on: